DDR1 autophosphorylation is a result of aggregation into dense clusters
- PMID: 31745115
- PMCID: PMC6863838
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-53176-4
DDR1 autophosphorylation is a result of aggregation into dense clusters
Abstract
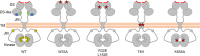
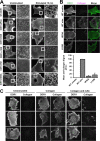
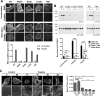
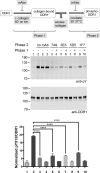
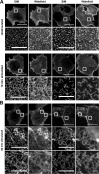
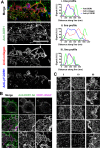
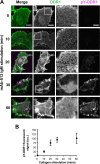
The collagen receptor DDR1 is a receptor tyrosine kinase that promotes progression of a wide range of human disorders. Little is known about how ligand binding triggers DDR1 kinase activity. We previously reported that collagen induces DDR1 activation through lateral dimer association and phosphorylation between dimers, a process that requires specific transmembrane association. Here we demonstrate ligand-induced DDR1 clustering by widefield and super-resolution imaging and provide evidence for a mechanism whereby DDR1 kinase activity is determined by its molecular density. Ligand binding resulted in initial DDR1 reorganisation into morphologically distinct clusters with unphosphorylated DDR1. Further compaction over time led to clusters with highly aggregated and phosphorylated DDR1. Ligand-induced DDR1 clustering was abolished by transmembrane mutations but did not require kinase activity. Our results significantly advance our understanding of the molecular events underpinning ligand-induced DDR1 kinase activity and provide an explanation for the unusually slow DDR1 activation kinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Collagen induces activation of DDR1 through lateral dimer association and phosphorylation between dimers.Elife. 2017 Jun 7;6:e25716. doi: 10.7554/eLife.25716. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28590245 Free PMC article.
-
Two-step release of kinase autoinhibition in discoidin domain receptor 1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Sep 8;117(36):22051-22060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2007271117. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32839343 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosylation at Asn211 regulates the activation state of the discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1).J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 28;289(13):9275-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.541102. Epub 2014 Feb 7. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24509848 Free PMC article.
-
Discoidin domain receptors: Micro insights into macro assemblies.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019 Nov;1866(11):118496. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2019.06.010. Epub 2019 Jun 21. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 31229648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A patent review of discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1) modulators (2014-present).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2020 May;30(5):341-350. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2020.1732925. Epub 2020 Feb 26. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2020. PMID: 32077340 Review.
Cited by
-
Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 functionally interacts with the IGF-I system in bladder cancer.Matrix Biol Plus. 2020 Jan 17;6-7:100022. doi: 10.1016/j.mbplus.2020.100022. eCollection 2020 May. Matrix Biol Plus. 2020. PMID: 33543020 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Cellular and Molecular Mechanism of Discoidin Domain Receptors (DDR1 and DDR2) in Bone Formation, Regeneration, and Its Associated Disease Conditions.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 4;24(19):14895. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914895. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Yin and Yang of Discoidin Domain Receptors (DDRs): Implications in Tumor Growth and Metastasis Development.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 6;13(7):1725. doi: 10.3390/cancers13071725. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33917302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Discoidin Domain Receptors DDR1 and DDR2 overcomes matrix-mediated tumor cell adaptation and tolerance to BRAF-targeted therapy in melanoma.EMBO Mol Med. 2022 Feb 7;14(2):e11814. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201911814. Epub 2021 Dec 27. EMBO Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 34957688 Free PMC article.
-
A two-site flexible clamp mechanism for RET-GDNF-GFRα1 assembly reveals both conformational adaptation and strict geometric spacing.Structure. 2021 Jul 1;29(7):694-708.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2020.12.012. Epub 2021 Jan 22. Structure. 2021. PMID: 33484636 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

