Chicken MBD4 Regulates Immunoglobulin Diversification by Somatic Hypermutation
- PMID: 31736964
- PMCID: PMC6838969
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02540
Chicken MBD4 Regulates Immunoglobulin Diversification by Somatic Hypermutation
Abstract
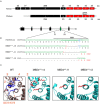
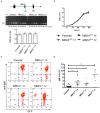
Immunoglobulin (Ig) diversification occurs via somatic hypermutation (SHM) and class switch recombination (CSR), and is initiated by activation-induced deaminase (AID), which converts cytosine to uracil. Variable (V) region genes undergo SHM to create amino acid substitutions that produce antibodies with higher affinity for antigen. The conversion of cytosine to uracil in DNA promotes mutagenesis. Two distinct DNA repair mechanisms regulate uracil processing in Ig genes. The first involves base removal by the uracil DNA glycosylase (UNG), and the second detects uracil via the mismatch repair (MMR) complex. Methyl binding domain protein 4 (MBD4) is a uracil glycosylase and an intriguing candidate for involvement in somatic hypermutation because of its interaction with the MMR MutL homolog 1 (MLH1). We found that the DNA uracil glycosylase domain of MBD4 is highly conserved among mammals, birds, shark, and insects. Conservation of the human and chicken MBD4 uracil glycosylase domain structure is striking. Here we examined the function of MBD4 in chicken DT40 B cells which undergo constitutive SHM. We constructed structural variants of MBD4 DT40 cells using CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing. Disruption of the MBD4 uracil glycosylase catalytic region increased SHM frequency in IgM loss assays. We propose that MBD4 plays a role in SHM.
Keywords: B cells; CRISPR; DT40; Ig; somatic hypermutation; uracil DNA glycosylase.
Copyright © 2019 Costello, Cantillo and Kenter.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cutting edge: the G-U mismatch glycosylase methyl-CpG binding domain 4 is dispensable for somatic hypermutation and class switch recombination.J Immunol. 2003 Feb 15;170(4):1620-4. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.4.1620. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12574322
-
Opinion: uracil DNA glycosylase (UNG) plays distinct and non-canonical roles in somatic hypermutation and class switch recombination.Int Immunol. 2014 Oct;26(10):575-8. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxu071. Epub 2014 Jul 3. Int Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24994819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA polymerases β and λ do not directly affect Ig variable region somatic hypermutation although their absence reduces the frequency of mutations.DNA Repair (Amst). 2013 Dec;12(12):1087-93. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2013.09.002. Epub 2013 Sep 29. DNA Repair (Amst). 2013. PMID: 24084171 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of S-region hypermutation and class-switch recombination by noncanonical functions of uracil DNA glycosylase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Mar 18;111(11):E1016-24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1402391111. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24591630 Free PMC article.
-
The contested role of uracil DNA glycosylase in immunoglobulin gene diversification.Trends Genet. 2005 May;21(5):253-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2005.02.013. Trends Genet. 2005. PMID: 15851057 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolutionary Comparative Analyses of DNA-Editing Enzymes of the Immune System: From 5-Dimensional Description of Protein Structures to Immunological Insights and Applications to Protein Engineering.Front Immunol. 2021 May 31;12:642343. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.642343. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34135887 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

