A comparative study of single-particle cryo-EM with liquid-nitrogen and liquid-helium cooling
- PMID: 31709065
- PMCID: PMC6830223
- DOI: 10.1107/S2052252519011503
A comparative study of single-particle cryo-EM with liquid-nitrogen and liquid-helium cooling
Abstract
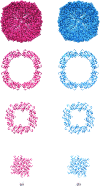
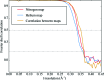
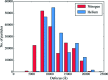
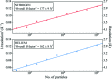
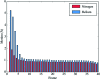
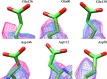
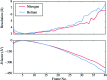
Radiation damage is the most fundamental limitation for achieving high resolution in electron cryo-microscopy (cryo-EM) of biological samples. The effects of radiation damage are reduced by liquid-helium cooling, although the use of liquid helium is more challenging than that of liquid nitrogen. To date, the benefits of liquid-nitrogen and liquid-helium cooling for single-particle cryo-EM have not been compared quantitatively. With recent technical and computational advances in cryo-EM image recording and processing, such a comparison now seems timely. This study aims to evaluate the relative merits of liquid-helium cooling in present-day single-particle analysis, taking advantage of direct electron detectors. Two data sets for recombinant mouse heavy-chain apoferritin cooled with liquid-nitrogen or liquid-helium to 85 or 17 K were collected, processed and compared. No improvement in terms of resolution or Coulomb potential map quality was found for liquid-helium cooling. Interestingly, beam-induced motion was found to be significantly higher with liquid-helium cooling, especially within the most valuable first few frames of an exposure, thus counteracting any potential benefit of better cryoprotection that liquid-helium cooling may offer for single-particle cryo-EM.
Keywords: apoferritin; beam-induced motion; beam-induced movement; cryo-EM; electron cryo-microscopy; helium; liquid-helium cooling; radiation damage.
© Olivia Pfeil-Gardiner et al. 2019.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Obtaining high-resolution images of biological macromolecules by using a cryo-electron microscope with a liquid-helium cooled stage.Micron. 2011 Feb;42(2):100-6. doi: 10.1016/j.micron.2010.08.006. Epub 2010 Sep 8. Micron. 2011. PMID: 20869255 Review.
-
A comparison of liquid nitrogen and liquid helium as cryogens for electron cryotomography.J Struct Biol. 2006 Mar;153(3):231-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2005.12.004. Epub 2006 Jan 4. J Struct Biol. 2006. PMID: 16427786
-
High-resolution single-particle cryo-EM of samples vitrified in boiling nitro-gen.IUCrJ. 2021 Sep 7;8(Pt 6):867-877. doi: 10.1107/S2052252521008095. eCollection 2021 Nov 1. IUCrJ. 2021. PMID: 34804541 Free PMC article.
-
A new cryo-EM system for single particle analysis.J Struct Biol. 2019 Jul 1;207(1):40-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2019.04.011. Epub 2019 Apr 13. J Struct Biol. 2019. PMID: 30991102
-
Setting up and operating a cryo-EM laboratory.Q Rev Biophys. 2021 Jan 8;54:e2. doi: 10.1017/S003358352000013X. Q Rev Biophys. 2021. PMID: 33413714 Review.
Cited by
-
Devitrification reduces beam-induced movement in cryo-EM.IUCrJ. 2021 Mar 1;8(Pt 2):186-194. doi: 10.1107/S2052252520016243. eCollection 2021 Mar 1. IUCrJ. 2021. PMID: 33708396 Free PMC article.
-
Forty years in cryoEM of membrane proteins.Microscopy (Oxf). 2022 Feb 18;71(Supplement_1):i30-i50. doi: 10.1093/jmicro/dfab041. Microscopy (Oxf). 2022. PMID: 35275191 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-electron tomography related radiation-damage parameters for individual-molecule 3D structure determination.Front Chem. 2022 Aug 30;10:889203. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.889203. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 36110139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into protein structure using cryogenic light microscopy.Biochem Soc Trans. 2023 Dec 20;51(6):2041-2059. doi: 10.1042/BST20221246. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023. PMID: 38015555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cryomicroscopy in situ: what is the smallest molecule that can be directly identified without labels in a cell?Faraday Discuss. 2022 Nov 8;240(0):277-302. doi: 10.1039/d2fd00076h. Faraday Discuss. 2022. PMID: 35913392 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

