Aurora-a confers radioresistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma by activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 31703572
- PMCID: PMC6842208
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-019-6312-y
Aurora-a confers radioresistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma by activating NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Radiotherapy failure is a significant clinical challenge due to the development of resistance in the course of treatment. Therefore, it is necessary to further study the radiation resistance mechanism of HCC. In our early study, we have showed that the expression of Aurora-A mRNA was upregulated in HCC tissue samples or cells, and Aurora-A promoted the malignant phenotype of HCC cells. However, the effect of Aurora-A on the development of HCC radioresistance is not well known.
Methods: In this study, colony formation assay, MTT assays, flow cytometry assays, RT-PCR assays, Western blot, and tumor xenografts experiments were used to identify Aurora-A promotes the radioresistance of HCC cells by decreasing IR-induced apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Dual-luciferase reporter assay, MTT assays, flow cytometry assays, and Western blot assay were performed to show the interactions of Aurora-A and NF-κB.
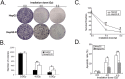
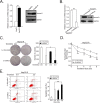
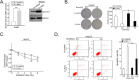
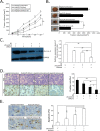
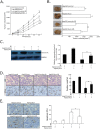
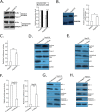
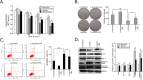
Results: We established radioresistance HCC cell lines (HepG2-R) and found that Aurora-A was significantly upregulated in those radioresistant HCC cells in comparison with their parental HCC cells. Knockdown of Aurora-A increased radiosensitivity of radioresistant HCC cells both in vivo and in vitro by enhancing irradiation-induced apoptosis, while upregulation of Aurora-A decreased radiosensitivity by reducing irradiation-induced apoptosis of parental cells. In addition, we have showed that Aurora-A could promote the expression of nuclear IkappaB-alpha (IκBα) protein while enhancing the activity of NF-kappaB (κB), thereby promoted expression of NF-κB pathway downstream effectors, including proteins (Mcl-1, Bcl-2, PARP, and caspase-3), all of which are associated with apoptosis.
Conclusions: Aurora-A reduces radiotherapy-induced apoptosis by activating NF-κB signaling, thereby contributing to HCC radioresistance. Our results provided the first evidence that Aurora-A was essential for radioresistance in HCC and targeting this molecular would be a potential strategy for radiosensitization in HCC.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Aurora-a; Hepatocellular carcinoma; NF-kappaB; Radioresistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Minichromosome maintenance 3 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma radioresistance by activating the NF-κB pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jun 17;38(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1241-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31208444 Free PMC article.
-
Aurora-A promotes chemoresistance in hepatocelluar carcinoma by targeting NF-kappaB/microRNA-21/PTEN signaling pathway.Oncotarget. 2014 Dec 30;5(24):12916-35. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2682. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25428915 Free PMC article.
-
ERCC6L promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through activating PI3K/AKT and NF-κB signaling pathway.BMC Cancer. 2020 Sep 5;20(1):853. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07367-2. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32891122 Free PMC article.
-
A new biomarker to enhance the radiosensitivity of hepatocellular cancer: miRNAs.Future Oncol. 2022 Sep;18(28):3217-3228. doi: 10.2217/fon-2022-0136. Epub 2022 Aug 15. Future Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35968820 Review.
-
An emerging role of radiation‑induced exosomes in hepatocellular carcinoma progression and radioresistance (Review).Int J Oncol. 2022 Apr;60(4):46. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2022.5336. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Int J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35266016 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Radiation-induced liver disease: beyond DNA damage.Cell Cycle. 2023 Mar;22(5):506-526. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2131163. Epub 2022 Oct 10. Cell Cycle. 2023. PMID: 36214587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatics screening the novel and promising targets of curcumin in hepatocellular carcinoma chemotherapy and prognosis.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Jan 25;22(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03487-9. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35078445 Free PMC article.
-
Bladder Cancer Treatments in the Age of Personalized Medicine: A Comprehensive Review of Potential Radiosensitivity Biomarkers.Biomark Insights. 2024 Nov 6;19:11772719241297168. doi: 10.1177/11772719241297168. eCollection 2024. Biomark Insights. 2024. PMID: 39512649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of Aurora-A in human cancers and future therapeutics.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Sep 1;10(9):2705-2729. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33042612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytochrome P450 1A2 overcomes nuclear factor kappa B-mediated sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncogene. 2021 Jan;40(3):492-507. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01545-z. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 33184472
References
-
- Mornex F, Girard N, Beziat C, Kubas A, Khodri M, Trepo C, Merle P. Feasibility and efficacy of high-dose three-dimensional-conformal radiotherapy in cirrhotic patients with small-size hepatocellular carcinoma non-eligible for curative therapies--mature results of the French phase II RTF-1 trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;66(4):1152–1158. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.06.015. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

