The Roles of MicroRNAs (miRNAs) in Avian Response to Viral Infection and Pathogenesis of Avian Immunosuppressive Diseases
- PMID: 31683847
- PMCID: PMC6862082
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20215454
The Roles of MicroRNAs (miRNAs) in Avian Response to Viral Infection and Pathogenesis of Avian Immunosuppressive Diseases
Abstract
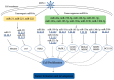
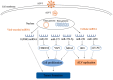
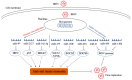
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of non-coding small RNAs that play important roles in the regulation of various biological processes including cell development and differentiation, apoptosis, tumorigenesis, immunoregulation and viral infections. Avian immunosuppressive diseases refer to those avian diseases caused by pathogens that target and damage the immune organs or cells of the host, increasing susceptibility to other microbial infections and the risk of failure in subsequent vaccination against other diseases. As such, once a disease with an immunosuppressive feature occurs in flocks, it would be difficult for the stakeholders to have an optimal economic income. Infectious bursal disease (IBD), avian leukemia (AL), Marek's disease (MD), chicken infectious anemia (CIA), reticuloendotheliosis (RE) and avian reovirus infection are on the top list of commonly-seen avian diseases with a feature of immunosuppression, posing an unmeasurable threat to the poultry industry across the globe. Understanding the pathogenesis of avian immunosuppressive disease is the basis for disease prevention and control. miRNAs have been shown to be involved in host response to pathogenic infections in chickens, including regulation of immunity, tumorigenesis, cell proliferation and viral replication. Here we summarize current knowledge on the roles of miRNAs in avian response to viral infection and pathogenesis of avian immunosuppressive diseases, in particular, MD, AL, IBD and RE.
Keywords: chickens; host response; immunosuppressive diseases; miRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of MicroRNAs in Host Defense against Infectious Bursal Disease Virus (IBDV) Infection: A Hidden Front Line.Viruses. 2020 May 14;12(5):543. doi: 10.3390/v12050543. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32423052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Economically important non-oncogenic immunosuppressive viral diseases of chicken--current status.Vet Res Commun. 2006 Jul;30(5):541-66. doi: 10.1007/s11259-006-3278-4. Vet Res Commun. 2006. PMID: 16883664 Review.
-
Viral diseases of the immune system and strategies to control infectious bursal disease by vaccination.Acta Vet Hung. 1997;45(3):239-49. Acta Vet Hung. 1997. PMID: 9276986 Review.
-
Genetic resistance to avian viruses.Rev Sci Tech. 1998 Apr;17(1):249-55. doi: 10.20506/rst.17.1.1082. Rev Sci Tech. 1998. PMID: 9638814 Review.
-
A multiplex xTAG assay for the simultaneous detection of five chicken immunosuppressive viruses.BMC Vet Res. 2018 Nov 15;14(1):347. doi: 10.1186/s12917-018-1663-1. BMC Vet Res. 2018. PMID: 30442149 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Avian Leucosis Virus-Host Interaction: The Involvement of Host Factors in Viral Replication.Front Immunol. 2022 May 26;13:907287. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.907287. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35693802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA expression profiling in the lungs of genetically different Ri chicken lines against the highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus.J Anim Sci Technol. 2023 Jul;65(4):838-855. doi: 10.5187/jast.2022.e127. Epub 2023 Jul 30. J Anim Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 37970505 Free PMC article.
-
miR-17-5p accelerates cervical cancer cells migration and invasion via the TIMP2/MMPs signaling cascade.Cytotechnology. 2021 Aug;73(4):619-627. doi: 10.1007/s10616-021-00482-3. Epub 2021 Jun 23. Cytotechnology. 2021. PMID: 34349351 Free PMC article.
-
Immune escape of avian oncogenic Marek's disease herpesvirus and antagonistic host immune responses.NPJ Vaccines. 2024 Jun 15;9(1):109. doi: 10.1038/s41541-024-00905-0. NPJ Vaccines. 2024. PMID: 38879650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Animal Health and Welfare in Livestock.Front Vet Sci. 2020 Dec 18;7:578193. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.578193. eCollection 2020. Front Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 33392281 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

