Small-Molecule MYC Inhibitors Suppress Tumor Growth and Enhance Immunotherapy
- PMID: 31679823
- PMCID: PMC6939458
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.10.001
Small-Molecule MYC Inhibitors Suppress Tumor Growth and Enhance Immunotherapy
Abstract
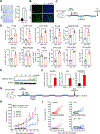
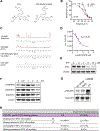
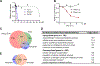
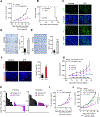
Small molecules that directly target MYC and are also well tolerated in vivo will provide invaluable chemical probes and potential anti-cancer therapeutic agents. We developed a series of small-molecule MYC inhibitors that engage MYC inside cells, disrupt MYC/MAX dimers, and impair MYC-driven gene expression. The compounds enhance MYC phosphorylation on threonine-58, consequently increasing proteasome-mediated MYC degradation. The initial lead, MYC inhibitor 361 (MYCi361), suppressed in vivo tumor growth in mice, increased tumor immune cell infiltration, upregulated PD-L1 on tumors, and sensitized tumors to anti-PD1 immunotherapy. However, 361 demonstrated a narrow therapeutic index. An improved analog, MYCi975 showed better tolerability. These findings suggest the potential of small-molecule MYC inhibitors as chemical probes and possible anti-cancer therapeutic agents.
Keywords: MYC; MYC degradation; MYC-threonine 58 phosphorylation; PD-L1; anti-PD1; cancer therapy; immunotherapy; in silico screen; small molecules; target engagement.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests
H.H., A.D.J., J.I., R.K.M. G.E.S. and S.A.A. are co-inventors on patent applications covering the methods and assays to identify and characterize MYC inhibitors and derivatives. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Communication between EMT and PD-L1 signaling: New insights into tumor immune evasion.Cancer Lett. 2020 Jan 1;468:72-81. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.10.013. Epub 2019 Oct 9. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 31605776 Review.
-
Turning Up the Heat on MYC: Progress in Small-Molecule Inhibitors.Cancer Res. 2021 Jan 15;81(2):248-253. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-2959. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33087323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Checkpoint Inhibition Followed by Tumor Infiltration of Dendritic Cells in Murine Neuro-2a Neuroblastoma.J Surg Res. 2020 Sep;253:201-213. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2020.03.059. Epub 2020 May 4. J Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 32380346
-
B7-H3 Negatively Modulates CTL-Mediated Cancer Immunity.Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Jun 1;24(11):2653-2664. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2852. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29530936
-
Nanomicelle protects the immune activation effects of Paclitaxel and sensitizes tumors to anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy.Theranostics. 2020 Jul 9;10(18):8382-8399. doi: 10.7150/thno.45391. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32724476 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cancer-cell-intrinsic mechanisms shaping the immunosuppressive landscape of prostate cancer.Asian J Androl. 2023 Mar-Apr;25(2):171-178. doi: 10.4103/aja202283. Asian J Androl. 2023. PMID: 36367020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory mechanisms of immune checkpoints PD-L1 and CTLA-4 in cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Jun 4;40(1):184. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01987-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34088360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WNT/β-catenin regulatory roles on PD-(L)1 and immunotherapy responses.Clin Exp Med. 2024 Jan 27;24(1):15. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01274-z. Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38280119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Strategies for Disrupting Cancer-Cell Functions with Mitochondria-Targeted Antitumor Drug-Loaded Nanoformulations.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Jun 9;16:3907-3936. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S303832. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34135584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lytic Induction Therapy against Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Malignancies: Past, Present, and Future.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 2;12(8):2142. doi: 10.3390/cancers12082142. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32748879 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baell JB, and Holloway GA (2010). New substructure filters for removal of pan assay interference compounds (PAINS) from screening libraries and for their exclusion in bioassays. J Med Chem 53, 2719–2740. - PubMed
-
- Blackwell TK, Kretzner L, Blackwood EM, Eisenman RN, and Weintraub H (1990). Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science 250, 1149–1151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

