Immunomodulatory Protein from Nectria haematococca Induces Apoptosis in Lung Cancer Cells via the P53 Pathway
- PMID: 31661772
- PMCID: PMC6862031
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20215348
Immunomodulatory Protein from Nectria haematococca Induces Apoptosis in Lung Cancer Cells via the P53 Pathway
Abstract
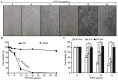
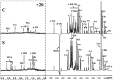
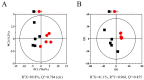
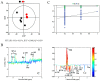
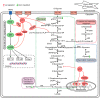
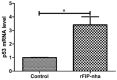
Our previous research has shown that a fungal immunomodulatory protein from Nectria haematococca (FIP-nha) possesses a wide spectrum of anti-tumor activities, and FIP-nha induced A549 apoptosis by negatively regulating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway based on comparative quantitative proteomics. This study further confirmed that the anti-lung cancer activity of FIP-nha was significantly stronger than that of the reported LZ-8 and FIP-fve. Subsequently, 1H NMR-based metabolomics was applied to comprehensively investigate the underlying mechanism, and a clear separation of FIP-nha-treated and untreated groups was achieved using pattern recognition analysis. Four potential pathways associated with the anti-tumor effect of FIP-nha on A549 cells were identified, and these were mainly involved in glycolysis, taurine and hypotaurine metabolism, fructose and mannose metabolism, and glycerolipid metabolism. Metabolic pathway analysis demonstrated that FIP-nha could induce A549 cell apoptosis partly by regulating the p53 inhibition pathway, which then disrupted the Warburg effect, as well as through other metabolic pathways. Using RT-PCR analysis, FIP-nha-induced apoptosis was confirmed to occur through upregulation of p53 expression. This work highlights the possible use of FIP-nha as a therapeutic adjuvant for lung cancer treatment.
Keywords: A549; NMR metabolomics; Nectria haematococca; fungal immunomodulatory protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
FIP-nha, a fungal immunomodulatory protein from Nectria haematococca, induces apoptosis and autophagy in human gastric cancer cells via blocking the EGFR-mediated STAT3/Akt signaling pathway.Food Chem (Oxf). 2022 Feb 25;4:100091. doi: 10.1016/j.fochms.2022.100091. eCollection 2022 Jul 30. Food Chem (Oxf). 2022. PMID: 35415679 Free PMC article.
-
Fungal Immunomodulatory Protein from Nectria haematococca Suppresses Growth of Human Lung Adenocarcinoma by Inhibiting the PI3K/Akt Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 1;19(11):3429. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113429. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30388826 Free PMC article.
-
Interruption of lung cancer cell migration and proliferation by fungal immunomodulatory protein FIP-fve from Flammulina velutipes.J Agric Food Chem. 2013 Dec 11;61(49):12044-52. doi: 10.1021/jf4030272. Epub 2013 Nov 22. J Agric Food Chem. 2013. PMID: 24274472
-
Recombinant expression of a novel fungal immunomodulatory protein with human tumor cell antiproliferative activity from Nectria haematococca.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Sep 30;15(10):17751-64. doi: 10.3390/ijms151017751. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25272229 Free PMC article.
-
New advances and potentials of fungal immunomodulatory proteins for therapeutic purposes.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2020 Dec;40(8):1172-1190. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2020.1808581. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32854547 Review.
Cited by
-
A Seven Immune-Related lncRNAs Model to Increase the Predicted Value of Lung Adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2020 Oct 14;10:560779. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.560779. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33163400 Free PMC article.
-
FIP-nha, a fungal immunomodulatory protein from Nectria haematococca, induces apoptosis and autophagy in human gastric cancer cells via blocking the EGFR-mediated STAT3/Akt signaling pathway.Food Chem (Oxf). 2022 Feb 25;4:100091. doi: 10.1016/j.fochms.2022.100091. eCollection 2022 Jul 30. Food Chem (Oxf). 2022. PMID: 35415679 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria-related lncRNAs: predicting prognosis, tumor microenvironment and treatment response in lung adenocarcinoma.Funct Integr Genomics. 2023 Oct 21;23(4):323. doi: 10.1007/s10142-023-01245-3. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37864709 Free PMC article.
-
A cuproptosis-related lncRNAs risk model to predict prognosis and guide immunotherapy for lung adenocarcinoma.Ann Transl Med. 2023 Mar 15;11(5):198. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-3195. Epub 2023 Mar 7. Ann Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37007546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen Y., Ma Z., Li A., Li H., Wang B., Zhong J., Min L., Dai L. Metabolomic profiling of human serum in lung cancer patients using liquid chromatography/hybrid quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015;141:705–718. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1846-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kino K., Yamashita A., Yamaoka K., Watanabe J., Tanaka S., Ko K., Shimizu K., Tsunoo H. Isolation and characterization of a new immunomodulatory protein, ling zhi-8 (LZ-8), from Ganoderma lucidium. J. Biol. Chem. 1989;264:472–478. - PubMed
-
- Li J., Cheng C., Yang W., Yang C., Ou Y., Wu M., Ko J. FIP-gts Potentiate Autophagic Cell Death Against Cisplatin-resistant Urothelial Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2014;34:2973–2983. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

