Nucleoside Tetra- and Pentaphosphates Prepared Using a Tetraphosphorylation Reagent Are Potent Inhibitors of Ribonuclease A
- PMID: 31651164
- PMCID: PMC7015663
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.9b09760
Nucleoside Tetra- and Pentaphosphates Prepared Using a Tetraphosphorylation Reagent Are Potent Inhibitors of Ribonuclease A
Abstract
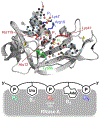
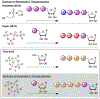
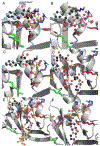
Adenosine and uridine 5'-tetra- and 5'-pentaphosphates were synthesized from an activated tetrametaphosphate ([PPN]2[P4O11], [PPN]2[1], PPN = bis(triphenylphosphine)iminium) and subsequently tested for inhibition of the enzymatic activity of ribonuclease A (RNase A). Reagent [PPN]2[1] reacts with unprotected uridine and adenosine in the presence of a base under anhydrous conditions to give nucleoside tetrametaphosphates. Ring opening of these intermediates with tetrabutylammonium hydroxide ([TBA][OH]) yields adenosine and uridine tetraphosphates (p4A, p4U) in 92% and 85% yields, respectively, from the starting nucleoside. Treatment of ([PPN]2[1]) with AMP or UMP yields nucleoside-monophosphate tetrametaphosphates (cp4pA, cp4pU) having limited aqueous stability. Ring opening of these ultraphosphates with [TBA][OH] yields p5A and p5U in 58% and 70% yield from AMP and UMP, respectively. We characterized inorganic and nucleoside-conjugated linear and cyclic oligophosphates as competitive inhibitors of RNase A. Increasing the chain length in both linear and cyclic inorganic oligophosphates resulted in improved binding affinity. Increasing the length of oligophosphates on the 5' position of adenosine beyond three had a deleterious effect on binding. Conversely, uridine nucleotides bearing 5' oligophosphates saw progressive increases in binding with chain length. We solved X-ray cocrystal structures of the highest affinity binders from several classes. The terminal phosphate of p5A binds in the P1 enzymic subsite and forces the oligophosphate to adopt a convoluted conformation, while the oligophosphate of p5U binds in several extended conformations, targeting multiple cationic regions of the active-site cleft.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): The tetraphosphorylation reagent is covered in patent US10017388B2.
Figures
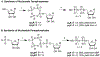
Similar articles
-
Synthesis of α,δ-Disubstituted Tetraphosphates and Terminally-Functionalized Nucleoside Pentaphosphates.J Am Chem Soc. 2021 Jan 13;143(1):463-470. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c11884. Epub 2020 Dec 29. J Am Chem Soc. 2021. PMID: 33375782 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution crystal structures of ribonuclease A complexed with adenylic and uridylic nucleotide inhibitors. Implications for structure-based design of ribonucleolytic inhibitors.Protein Sci. 2003 Nov;12(11):2559-74. doi: 10.1110/ps.03196603. Protein Sci. 2003. PMID: 14573867 Free PMC article.
-
5'-Modified pyrimidine nucleosides as inhibitors of ribonuclease A.Bioorg Med Chem. 2011 Apr 1;19(7):2478-84. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2010.08.059. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Bioorg Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21420869
-
Beyond Triphosphates: Reagents and Methods for Chemical Oligophosphorylation.J Am Chem Soc. 2022 May 4;144(17):7517-7530. doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c07990. Epub 2022 Apr 26. J Am Chem Soc. 2022. PMID: 35471019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Structures and functions of ribonucleases].Yakugaku Zasshi. 1997 Sep;117(9):561-82. doi: 10.1248/yakushi1947.117.9_561. Yakugaku Zasshi. 1997. PMID: 9357326 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The Aryne Phosphate Reaction.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022 Jan 3;61(1):e202113231. doi: 10.1002/anie.202113231. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022. PMID: 34727582 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of α,δ-Disubstituted Tetraphosphates and Terminally-Functionalized Nucleoside Pentaphosphates.J Am Chem Soc. 2021 Jan 13;143(1):463-470. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c11884. Epub 2020 Dec 29. J Am Chem Soc. 2021. PMID: 33375782 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Phosphate Granules Contain Cyclic Polyphosphates: Evidence from 31P Solid-State NMR.J Am Chem Soc. 2020 Oct 28;142(43):18407-18421. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c06335. Epub 2020 Oct 19. J Am Chem Soc. 2020. PMID: 33075224 Free PMC article.
-
Preventing lipophilic aggregation in cosolvent molecular dynamics simulations with hydrophobic probes using Plumed Automatic Restraining Tool (PART).J Cheminform. 2024 Feb 27;16(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13321-024-00819-y. J Cheminform. 2024. PMID: 38414037 Free PMC article.
-
Selective cleavage of ncRNA and antiviral activity by RNase2/EDN in THP1-induced macrophages.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Mar 26;79(4):209. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04229-x. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35347428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marshall GR; Feng JA; Kuster DJ Back to the future: ribonuclease A. Biopolymers 2008, 90, 259–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

