Neto proteins regulate gating of the kainate-type glutamate receptor GluK2 through two binding sites
- PMID: 31628192
- PMCID: PMC6879349
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.008631
Neto proteins regulate gating of the kainate-type glutamate receptor GluK2 through two binding sites
Abstract
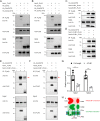
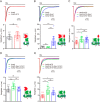
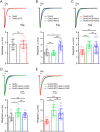
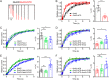
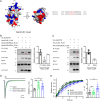
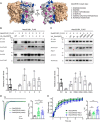
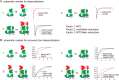
The neuropilin and tolloid-like (Neto) proteins Neto1 and Neto2 are auxiliary subunits of kainate-type glutamate receptors (KARs) that regulate KAR trafficking and gating. However, how Netos bind and regulate the biophysical functions of KARs remains unclear. Here, we found that the N-terminal domain (NTD) of glutamate receptor ionotropic kainate 2 (GluK2) binds the first complement C1r/C1s-Uegf-BMP (CUB) domain of Neto proteins (i.e. NTD-CUB1 interaction) and that the core of GluK2 (GluK2ΔNTD) binds Netos through domains other than CUB1s (core-Neto interaction). Using electrophysiological analysis in HEK293T cells, we examined the effects of these interactions on GluK2 gating, including deactivation, desensitization, and recovery from desensitization. We found that NTD deletion does not affect GluK2 fast gating kinetics, the desensitization, and the deactivation. We also observed that Neto1 and Neto2 differentially regulate GluK2 fast gating kinetics, which largely rely on the NTD-CUB1 interactions. NTD removal facilitated GluK2 recovery from desensitization, indicating that the NTD stabilizes the GluK2 desensitization state. Co-expression with Neto1 or Neto2 also accelerated GluK2 recovery from desensitization, which fully relied on the NTD-CUB1 interactions. Moreover, we demonstrate that the NTD-CUB1 interaction involves electric attraction between positively charged residues in the GluK2_NTD and negatively charged ones in the CUB1 domains. Neutralization of these charges eliminated the regulatory effects of the NTD-CUB1 interaction on GluK2 gating. We conclude that KARs bind Netos through at least two sites and that the NTD-CUB1 interaction critically regulates Neto-mediated GluK2 gating.
Keywords: CUB domain; N-terminal domain (NTD); allosteric regulation; channel gating; deactivation; desensitization; gating; glutamate ionotropic receptor kainate type subunit 2 (GriK2); glutamate receptor ionotropic kainate 2 (GluK2); ionotropic glutamate receptor; kainate receptor; neuropilin and tolloid-like (Neto); protein-protein interaction; receptor desensitization; recovery from desensitization.
© 2019 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of critical functional determinants of kainate receptor modulation by auxiliary protein Neto2.J Physiol. 2015 Nov 15;593(22):4815-33. doi: 10.1113/JP271103. Epub 2015 Sep 20. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26282342 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of homomeric and heteromeric kainate receptors by the auxiliary subunit Neto1.J Physiol. 2013 Oct 1;591(19):4711-24. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.256776. Epub 2013 Jun 24. J Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23798491 Free PMC article.
-
The auxiliary subunits Neto1 and Neto2 have distinct, subunit-dependent effects at recombinant GluK1- and GluK2-containing kainate receptors.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Dec;99:471-80. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.08.018. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 26277340 Free PMC article.
-
Neto2 Influences on Kainate Receptor Pharmacology and Function.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016 Aug;119(2):141-8. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.12575. Epub 2016 Mar 18. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26928870 Review.
-
Neto1 and Neto2: auxiliary subunits that determine key properties of native kainate receptors.J Physiol. 2012 May 15;590(10):2217-23. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.221101. Epub 2012 Mar 19. J Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22431337 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The atypical 'hippocampal' glutamate receptor coupled to phospholipase D that controls stretch-sensitivity in primary mechanosensory nerve endings is homomeric purely metabotropic GluK2.Exp Physiol. 2024 Jan;109(1):81-99. doi: 10.1113/EP090761. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Exp Physiol. 2024. PMID: 37656490 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysfunction of AMPA receptor GluA3 is associated with aggressive behavior in human.Mol Psychiatry. 2022 Oct;27(10):4092-4102. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01659-8. Epub 2022 Jun 13. Mol Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35697757
-
Kainate receptor modulation by NETO2.Nature. 2021 Nov;599(7884):325-329. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03936-y. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Nature. 2021. PMID: 34552241
-
Structure, Function, and Regulation of the Kainate Receptor.Subcell Biochem. 2022;99:317-350. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-00793-4_10. Subcell Biochem. 2022. PMID: 36151381 Review.
-
Structure, Function, and Pharmacology of Glutamate Receptor Ion Channels.Pharmacol Rev. 2021 Oct;73(4):298-487. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.120.000131. Pharmacol Rev. 2021. PMID: 34753794 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

