Obesity-linked suppression of membrane-bound O-acyltransferase 7 (MBOAT7) drives non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 31621579
- PMCID: PMC6850774
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.49882
Obesity-linked suppression of membrane-bound O-acyltransferase 7 (MBOAT7) drives non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
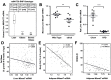
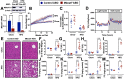
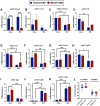
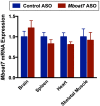
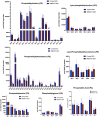
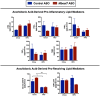
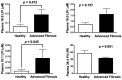
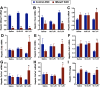
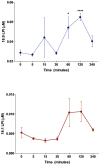
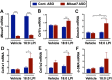
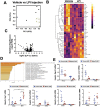
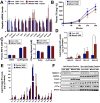
Recent studies have identified a genetic variant rs641738 near two genes encoding membrane bound O-acyltransferase domain-containing 7 (MBOAT7) and transmembrane channel-like 4 (TMC4) that associate with increased risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), alcohol-related cirrhosis, and liver fibrosis in those infected with viral hepatitis (Buch et al., 2015; Mancina et al., 2016; Luukkonen et al., 2016; Thabet et al., 2016; Viitasalo et al., 2016; Krawczyk et al., 2017; Thabet et al., 2017). Based on hepatic expression quantitative trait loci analysis, it has been suggested that MBOAT7 loss of function promotes liver disease progression (Buch et al., 2015; Mancina et al., 2016; Luukkonen et al., 2016; Thabet et al., 2016; Viitasalo et al., 2016; Krawczyk et al., 2017; Thabet et al., 2017), but this has never been formally tested. Here we show that Mboat7 loss, but not Tmc4, in mice is sufficient to promote the progression of NAFLD in the setting of high fat diet. Mboat7 loss of function is associated with accumulation of its substrate lysophosphatidylinositol (LPI) lipids, and direct administration of LPI promotes hepatic inflammatory and fibrotic transcriptional changes in an Mboat7-dependent manner. These studies reveal a novel role for MBOAT7-driven acylation of LPI lipids in suppressing the progression of NAFLD.
Keywords: NAFLD; hepatology; human biology; medicine; mouse; triacylglycerol.
© 2019, Helsley et al.
Conflict of interest statement
RH, VV, AB, AG, RS, IR, KF, MK, RB, CN, CF, PP, DO, LO, WM, RZ, AK, BS, CP, JS, ML, VG, JK, DA, MC, PF, LR, AL, MS, JB No competing interests declared, RL, RC, MG employee at Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Inc
Figures
Similar articles
-
The MBOAT7-TMC4 Variant rs641738 Increases Risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Individuals of European Descent.Gastroenterology. 2016 May;150(5):1219-1230.e6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.01.032. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Gastroenterology. 2016. PMID: 26850495 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of hepatic Mboat7 leads to liver fibrosis.Gut. 2021 May;70(5):940-950. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-320853. Epub 2020 Jun 26. Gut. 2021. PMID: 32591434 Free PMC article.
-
Association between MBOAT7 rs641738 polymorphism and non-alcoholic fatty liver in overweight or obese children.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2021 May 6;31(5):1548-1555. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2021.01.020. Epub 2021 Feb 4. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2021. PMID: 33810963
-
Membrane-bound O-acyltransferase 7 (MBOAT7)-driven phosphatidylinositol remodeling in advanced liver disease.J Lipid Res. 2022 Jul;63(7):100234. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2022.100234. Epub 2022 May 27. J Lipid Res. 2022. PMID: 35636492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MBOAT7 down-regulation by genetic and environmental factors predisposes to MAFLD.EBioMedicine. 2020 Jul;57:102866. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102866. Epub 2020 Jul 3. EBioMedicine. 2020. PMID: 32629394 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MBOAT7-TMC4 rs641738 Is Not Associated With the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma or Persistent Hepatitis B Infection.Front Oncol. 2021 May 25;11:639438. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.639438. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34113561 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Metabolite Signatures in Male Carriers of Genetic Variants Associated with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Metabolites. 2023 Feb 13;13(2):267. doi: 10.3390/metabo13020267. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 36837886 Free PMC article.
-
Omics-derived hepatocellular carcinoma risk biomarkers for precision care of chronic liver diseases.Hepatol Res. 2020 Jul;50(7):817-830. doi: 10.1111/hepr.13506. Epub 2020 May 15. Hepatol Res. 2020. PMID: 32323426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolomics and lipidomics in NAFLD: biomarkers and non-invasive diagnostic tests.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Dec;18(12):835-856. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00502-9. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34508238 Review.
-
AS160 is a lipid-responsive regulator of cardiac Ca2+ homeostasis by controlling lysophosphatidylinositol metabolism and signaling.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 6;15(1):9602. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54031-5. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39505896 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown JM, Boysen MS, Jensen SS, Morrison RF, Storkson J, Lea-Currie R, Pariza M, Mandrup S, McIntosh MK. Isomer-specific regulation of metabolism and PPARgamma signaling by CLA in human preadipocytes. Journal of Lipid Research. 2003;44:1287–1300. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M300001-JLR200. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01 DK120679/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL106173/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061732/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R00-HL12172/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL147823/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01-HL30568/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F32-HL136044/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AA021893/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK103637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AR067477/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL122283/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA024333/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL030568/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL136044/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL122283/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01-HL49373/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK120679/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA021893/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA150964/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM095467/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL106173/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA043703/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL029582/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50-AA-024333/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK103637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK061732/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL049373/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

