Cooperative DNA binding by proteins through DNA shape complementarity
- PMID: 31616952
- PMCID: PMC7145599
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkz642
Cooperative DNA binding by proteins through DNA shape complementarity
Abstract
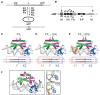
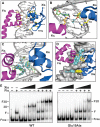
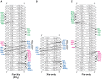
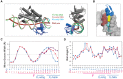
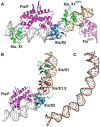
Localized arrays of proteins cooperatively assemble onto chromosomes to control DNA activity in many contexts. Binding cooperativity is often mediated by specific protein-protein interactions, but cooperativity through DNA structure is becoming increasingly recognized as an additional mechanism. During the site-specific DNA recombination reaction that excises phage λ from the chromosome, the bacterial DNA architectural protein Fis recruits multiple λ-encoded Xis proteins to the attR recombination site. Here, we report X-ray crystal structures of DNA complexes containing Fis + Xis, which show little, if any, contacts between the two proteins. Comparisons with structures of DNA complexes containing only Fis or Xis, together with mutant protein and DNA binding studies, support a mechanism for cooperative protein binding solely by DNA allostery. Fis binding both molds the minor groove to potentiate insertion of the Xis β-hairpin wing motif and bends the DNA to facilitate Xis-DNA contacts within the major groove. The Fis-structured minor groove shape that is optimized for Xis binding requires a precisely positioned pyrimidine-purine base-pair step, whose location has been shown to modulate minor groove widths in Fis-bound complexes to different DNA targets.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fis targets assembly of the Xis nucleoprotein filament to promote excisive recombination by phage lambda.J Mol Biol. 2007 Mar 23;367(2):328-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.12.071. Epub 2007 Jan 3. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17275024 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the cooperative Xis-DNA complex reveals a micronucleoprotein filament that regulates phage lambda intasome assembly.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Feb 13;104(7):2109-14. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0607820104. Epub 2007 Feb 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17287355 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of directionality in bacteriophage lambda site-specific recombination: structure of the Xis protein.J Mol Biol. 2002 Dec 6;324(4):791-805. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)01150-6. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12460578
-
Bacteriophage lambda site-specific recombination.Mol Microbiol. 2024 May;121(5):895-911. doi: 10.1111/mmi.15241. Epub 2024 Feb 19. Mol Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38372210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integration of syntactic and semantic properties of the DNA code reveals chromosomes as thermodynamic machines converting energy into information.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Dec;70(23):4555-67. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1394-1. Epub 2013 Jun 15. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23771629 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mycobacteriophage Alexphander Gene 94 Encodes an Essential dsDNA-Binding Protein during Lytic Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 7;25(13):7466. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137466. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000573 Free PMC article.
-
A bacteriophage mimic of the bacterial nucleoid-associated protein Fis.Biochem J. 2020 Apr 17;477(7):1345-1362. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20200146. Biochem J. 2020. PMID: 32207815 Free PMC article.
-
Allostery through DNA drives phenotype switching.Nat Commun. 2021 May 20;12(1):2967. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23148-2. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34016970 Free PMC article.
-
The DNA relaxation-dependent OFF-to-ON biasing of the type 1 fimbrial genetic switch requires the Fis nucleoid-associated protein.Microbiology (Reading). 2023 Jan;169(1):001283. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001283. Microbiology (Reading). 2023. PMID: 36748578 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Shape Deformation of DNA-Binding Sites in Regulating the Efficiency and Specificity in Their Recognition by DNA-Binding Proteins.JACS Au. 2024 Jun 18;4(7):2640-2655. doi: 10.1021/jacsau.4c00393. eCollection 2024 Jul 22. JACS Au. 2024. PMID: 39055163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thompson J.F., Landy A.. Berg D, Howe M. Mobile DNA. 1989; Washington: ASM Press; 1–22.

