Voltage-dependent activation of Rac1 by Nav 1.5 channels promotes cell migration
- PMID: 31612502
- PMCID: PMC6973152
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.29290
Voltage-dependent activation of Rac1 by Nav 1.5 channels promotes cell migration
Abstract
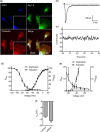
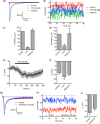
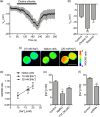
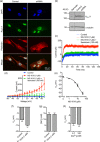
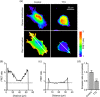
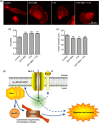
Ion channels can regulate the plasma membrane potential (Vm ) and cell migration as a result of altered ion flux. However, the mechanism by which Vm regulates motility remains unclear. Here, we show that the Nav 1.5 sodium channel carries persistent inward Na+ current which depolarizes the resting Vm at the timescale of minutes. This Nav 1.5-dependent Vm depolarization increases Rac1 colocalization with phosphatidylserine, to which it is anchored at the leading edge of migrating cells, promoting Rac1 activation. A genetically encoded FRET biosensor of Rac1 activation shows that depolarization-induced Rac1 activation results in acquisition of a motile phenotype. By identifying Nav 1.5-mediated Vm depolarization as a regulator of Rac1 activation, we link ionic and electrical signaling at the plasma membrane to small GTPase-dependent cytoskeletal reorganization and cellular migration. We uncover a novel and unexpected mechanism for Rac1 activation, which fine tunes cell migration in response to ionic and/or electric field changes in the local microenvironment.
Keywords: Nav1.5; Rac1; breast cancer; membrane potential; migration.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular Physiology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Contribution of sodium channels to lamellipodial protrusion and Rac1 and ERK1/2 activation in ATP-stimulated microglia.Glia. 2014 Dec;62(12):2080-95. doi: 10.1002/glia.22728. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Glia. 2014. PMID: 25043721
-
SOX2 promotes hypoxia-induced breast cancer cell migration by inducing NEDD9 expression and subsequent activation of Rac1/HIF-1α signaling.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2019 Aug 22;24:55. doi: 10.1186/s11658-019-0180-y. eCollection 2019. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31462898 Free PMC article.
-
ARF1 controls Rac1 signaling to regulate migration of MDA-MB-231 invasive breast cancer cells.Cell Signal. 2013 Sep;25(9):1813-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.05.011. Epub 2013 May 23. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23707487
-
Structure-based assessment of disease-related mutations in human voltage-gated sodium channels.Protein Cell. 2017 Jun;8(6):401-438. doi: 10.1007/s13238-017-0372-z. Epub 2017 Feb 1. Protein Cell. 2017. PMID: 28150151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rac1: A Regulator of Cell Migration and a Potential Target for Cancer Therapy.Molecules. 2023 Mar 27;28(7):2976. doi: 10.3390/molecules28072976. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37049739 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Functional Role of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Nav1.5 in Metastatic Breast Cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jul 23;11:1111. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01111. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32792949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic targeting of voltage-gated sodium channel NaV1.7 for cancer metastasis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 9;15:1416705. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1416705. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39045054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of lidocaine in cancer progression and patient survival.Pharmacol Ther. 2024 Jul;259:108654. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2024.108654. Epub 2024 May 1. Pharmacol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38701900 Review.
-
Modulating voltage-gated sodium channels to enhance differentiation and sensitize glioblastoma cells to chemotherapy.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Sep 9;22(1):434. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01819-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39251990 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium accumulation in breast cancer predicts malignancy and treatment response.Br J Cancer. 2022 Jul;127(2):337-349. doi: 10.1038/s41416-022-01802-w. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Br J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35462561 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Antonov, A. S. , Antonova, G. N. , Fujii, M. , ten Dijke, P. , Handa, V. , Catravas, J. D. , & Verin, A. D. (2012). Regulation of endothelial barrier function by TGF‐β type I receptor ALK5: Potential role of contractile mechanisms and heat shock protein 90. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 227(2), 759–771. 10.1002/jcp.22785 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baldassa, S. , Zippel, R. , & Sturani, E. (2003). Depolarization‐induced signaling to Ras, Rap1 and MAPKs in cortical neurons. Brain Research: Molecular Brain Research, 119(1), 111–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

