Construction of a lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network to determine the regulatory roles of lncRNAs in psoriasis
- PMID: 31611939
- PMCID: PMC6781786
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.8035
Construction of a lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network to determine the regulatory roles of lncRNAs in psoriasis
Abstract
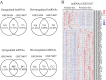
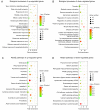
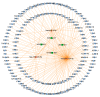
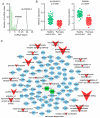
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder that impairs the quality of life of affected patients. Emerging studies indicate that certain long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have important roles in psoriasis. However, the exact functions of lncRNAs and their regulatory mechanisms as competitive endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) in psoriasis have remained to be fully elucidated. In the present study, differentially expressed lncRNAs, microRNAs (miRNAs) and mRNAs were identified by analyzing public datasets, and a psoriasis-associated lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network was constructed based on the ceRNA theory. Furthermore, previously validated abnormally expressed miRNAs in psoriasis were identified by a systematic literature search in the PubMed and Web of Science databases, and a specific miRNA-associated lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA sub-network was extracted. Furthermore, Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analyses were performed using DAVID 6.8. A total of 253 lncRNAs, 106 miRNAs and 1,156 mRNAs were identified as being differentially expressed between psoriasis skin and healthy control skin. The present study identified two key lncRNAs that may potentially have a role in the pathogenesis of psoriasis: AL035425.3 and Prader Willi/Angelman region RNA 6. This integrative analysis enhances the understanding of the molecular mechanism of psoriasis and may provide novel therapeutic targets for the treatment of psoriasis.
Keywords: competing endogenous RNAs; long non-coding RNAs; network; psoriasis.
Copyright: © Zhou et al.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Analysis of lncRNA-Associated ceRNA Network Reveals Potential lncRNA Biomarkers in Human Colon Adenocarcinoma.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49(5):1778-1791. doi: 10.1159/000493623. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30231249
-
Construction of chronic glomerulonephritis‑related lncRNA‑mRNA regulatory network and lncRNA‑-miRNA‑mRNA ceRNA network by bioinformatics analysis.Exp Ther Med. 2023 Jul 7;26(2):403. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.12102. eCollection 2023 Aug. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37522060 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of Prognostic lncRNAs, miRNAs, and mRNAs Forming a Competing Endogenous RNA Network in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(5):1953-1967. doi: 10.1159/000492519. Epub 2018 Aug 9. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30092571
-
Reconstruction and Analysis of the Differentially Expressed IncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network Based on Competitive Endogenous RNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019;29(6):539-549. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2019028740. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019. PMID: 32422009 Review.
-
[Long Non-Coding RNAs as Competitive Endogenous RNAs in Osteosarcoma].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2020 Sep-Oct;54(5):776-801. doi: 10.31857/S0026898420050055. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2020. PMID: 33009789 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
The lncRNA H19/miR-766-3p/S1PR3 Axis Contributes to the Hyperproliferation of Keratinocytes and Skin Inflammation in Psoriasis via the AKT/mTOR Pathway.Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Dec 28;2021:9991175. doi: 10.1155/2021/9991175. eCollection 2021. Mediators Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 34992498 Free PMC article.
-
miR-145-5p inhibits psoriasis progression by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Sep 15;13(9):10439-10448. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34650713 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of lncRNAs associated with the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 Mar 12;22(1):272. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04119-6. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021. PMID: 33711974 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNAs in immunoregulation and autoimmunity: Technological advances and critical limitations.J Autoimmun. 2023 Jan;134:102982. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2022.102982. Epub 2022 Dec 31. J Autoimmun. 2023. PMID: 36592512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The LINC01176-miR-218-5p-IL-36G Network is Responsible for the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis by Promoting Inflammation.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024 Jan 3;17:1-12. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S444265. eCollection 2024. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38193028 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
