Isoflurane mediated neuropathological and cognitive impairments in the triple transgenic Alzheimer's mouse model are associated with hippocampal synaptic deficits in an age-dependent manner
- PMID: 31600350
- PMCID: PMC6786564
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223509
Isoflurane mediated neuropathological and cognitive impairments in the triple transgenic Alzheimer's mouse model are associated with hippocampal synaptic deficits in an age-dependent manner
Abstract
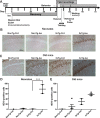
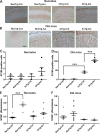
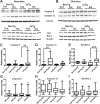
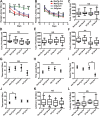
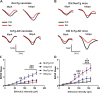
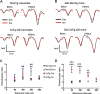
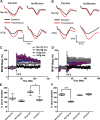
Many in vivo studies suggest that inhalational anesthetics can accelerate or prevent the progression of neuropathology and cognitive impairments in Alzheimer Disease (AD), but the synaptic mechanisms mediating these ambiguous effects are unclear. Here, we show that repeated exposures of neonatal and old triple transgenic AD (3xTg) and non-transgenic (NonTg) mice to isoflurane (Iso) distinctly increased neurodegeneration as measured by S100β levels, intracellular Aβ, Tau oligomerization, and apoptotic markers. Spatial cognition measured by reference and working memory testing in the Morris Water Maze (MWM) were altered in young NonTg and 3xTg. Field recordings in the cornu ammonis 1 (CA1) hippocampus showed that neonatal control 3xTg mice exhibited hypo-excitable synaptic transmission, reduced paired-pulse facilitation (PPF), and normal long-term potentiation (LTP) compared to NonTg controls. By contrast, the old control 3xTg mice exhibited hyper-excitable synaptic transmission, enhanced PPF, and unstable LTP compared to NonTg controls. Repeated Iso exposures reduced synaptic transmission and PPF in neonatal NonTg and old 3xTg mice. LTP was normalized in old 3xTg mice, but reduced in neonates. By contrast, LTP was reduced in old but not neonatal NonTg mice. Our results indicate that Iso-mediated neuropathologic and cognitive defects in AD mice are associated with synaptic pathologies in an age-dependent manner. Based on these findings, the extent of this association with age and, possibly, treatment paradigms warrant further study.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alterations in synaptic plasticity coincide with deficits in spatial working memory in presymptomatic 3xTg-AD mice.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2015 Nov;125:152-162. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2015.09.003. Epub 2015 Sep 15. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2015. PMID: 26385257 Free PMC article.
-
Adiponectin Ameliorates Cognitive Behaviors and in vivo Synaptic Plasticity Impairments in 3xTg-AD Mice.J Alzheimers Dis. 2022;85(1):343-357. doi: 10.3233/JAD-215063. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022. PMID: 34806605
-
Partial Inhibition of Mitochondrial Complex I Reduces Tau Pathology and Improves Energy Homeostasis and Synaptic Function in 3xTg-AD Mice.J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;79(1):335-353. doi: 10.3233/JAD-201015. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021. PMID: 33285637 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic Alterations in Mouse Models for Alzheimer Disease-A Special Focus on N-Truncated Abeta 4-42.Molecules. 2018 Mar 21;23(4):718. doi: 10.3390/molecules23040718. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29561816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hippocampal plasticity during the progression of Alzheimer's disease.Neuroscience. 2015 Nov 19;309:51-67. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.03.006. Epub 2015 Mar 12. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 25772787 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential hippocampal protein expression between normal mice and mice with the perioperative neurocognitive disorder: a proteomic analysis.Eur J Med Res. 2021 Nov 3;26(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s40001-021-00599-3. Eur J Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34732255 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma BDNF Levels Following Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Allow Prediction of Synaptic Plasticity and Memory Deficits in 3×Tg-AD Mice.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jul 3;8:541. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00541. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32719795 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic Plasticity and Oscillations in Alzheimer's Disease: A Complex Picture of a Multifaceted Disease.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Jun 17;14:696476. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.696476. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34220451 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting galectin-3 to counteract spike-phase uncoupling of fast-spiking interneurons to gamma oscillations in Alzheimer's disease.Transl Neurodegener. 2023 Feb 6;12(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s40035-023-00338-0. Transl Neurodegener. 2023. PMID: 36740709 Free PMC article.
-
Auditory sensory deprivation induced by noise exposure exacerbates cognitive decline in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Elife. 2021 Oct 26;10:e70908. doi: 10.7554/eLife.70908. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34699347 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee TA, Wolozin B, Weiss KB, Bednar MM. Assessment of the emergence of Alzheimer's disease following coronary artery bypass graft surgery or percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. J Alzheimers Dis. 2005;7(4):319–24. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

