Redox regulation of tyrosine kinase signalling: more than meets the eye
- PMID: 31599960
- PMCID: PMC6988750
- DOI: 10.1093/jb/mvz085
Redox regulation of tyrosine kinase signalling: more than meets the eye
Abstract
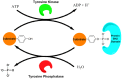
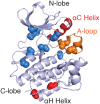
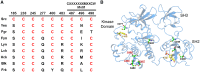
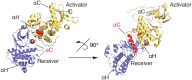
Protein kinases are essential mediators of cellular signal transduction and are often dysregulated in disease. Among these, protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs) have received specific interest due to their common roles in various diseases including cancer, and emerging observations indicating that PTK signalling pathways are susceptible to regulation by reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are also frequently implicated in disease pathology. While it is well recognized that ROS can impact on tyrosine kinase signalling by inhibiting tyrosine phosphatases, more recent studies highlight additional modes of redox-based regulation of tyrosine kinase signalling by direct redox modification of non-catalytic cysteines within tyrosine kinases or other protein components of this signalling pathway. In this review, we will present recent advancements with respect to redox-based mechanisms in regulating PTK signalling, with a specific focus on recent studies demonstrating direct redox regulation of Src-family kinases and epidermal growth factor receptor kinases. Importantly, redox-based modulation of tyrosine kinases may be relevant for many other kinases and has implications for current approaches to develop pharmacological inhibitors for these proteins.
Keywords: Redox; Src; EGFR; NOX; cysteine.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Japanese Biochemical Society. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Direct and specific inactivation of protein tyrosine kinases in the Src and FGFR families by reversible cysteine oxidation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Mar 31;106(13):5070-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0806117106. Epub 2009 Mar 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19273857 Free PMC article.
-
Redox-linked signal transduction pathways for protein tyrosine kinase activation.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2002 Jun;4(3):517-31. doi: 10.1089/15230860260196326. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2002. PMID: 12215220 Review.
-
Redox regulation of protein kinases.FEBS J. 2013 May;280(9):1944-65. doi: 10.1111/febs.12224. Epub 2013 Mar 21. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 23461806 Review.
-
Reactive oxygen species as essential mediators of cell adhesion: the oxidative inhibition of a FAK tyrosine phosphatase is required for cell adhesion.J Cell Biol. 2003 Jun 9;161(5):933-44. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200211118. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12796479 Free PMC article.
-
Redox modulation of tyrosine phosphorylation-dependent signal transduction pathways.Free Radic Biol Med. 1996;21(3):323-33. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(96)00051-2. Free Radic Biol Med. 1996. PMID: 8855443 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidation-Dependent Activation of Src Kinase Mediates Epithelial IL-33 Production and Signaling during Acute Airway Allergen Challenge.J Immunol. 2021 Jun 15;206(12):2989-2999. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000995. Epub 2021 Jun 4. J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34088769 Free PMC article.
-
Superoxide Radicals in the Execution of Cell Death.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Mar 4;11(3):501. doi: 10.3390/antiox11030501. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physiological Signaling Functions of Reactive Oxygen Species in Stem Cells: From Flies to Man.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 6;9:714370. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.714370. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34422833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative In Vitro Toxicology of Novel Cytoprotective Short-Chain Naphthoquinones.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Aug 7;13(8):184. doi: 10.3390/ph13080184. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32784558 Free PMC article.
-
FOXO nuclear shuttling dynamics are stimulus-dependent and correspond with cell fate.Mol Biol Cell. 2023 Mar 1;34(3):ar21. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E22-05-0193. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Mol Biol Cell. 2023. PMID: 36735481 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Endicott J.A., Noble M.E., Johnson L.N. (2012) The structural basis for control of eukaryotic protein kinases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 81, 587–613 - PubMed
-
- Pawson T., Gish G.D., Nash P. (2001) SH2 domains, interaction modules and cellular wiring. Trends Cell Biol. 11, 504–511 - PubMed
-
- Barford D., Das A.K., Egloff M.P. (1998) The structure and mechanism of protein phosphatases: insights into catalysis and regulation. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 27, 133–164 - PubMed
-
- Zhang J., Yang P.L., Gray N.S. (2009) Targeting cancer with small molecule kinase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Cancer 9, 28–39 - PubMed
-
- Holmstrom K.M., Finkel T. (2014) Cellular mechanisms and physiological consequences of redox-dependent signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 15, 411–421 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

