Tiam1 is Critical for Glutamatergic Synapse Structure and Function in the Hippocampus
- PMID: 31597723
- PMCID: PMC6867819
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1566-19.2019
Tiam1 is Critical for Glutamatergic Synapse Structure and Function in the Hippocampus
Abstract
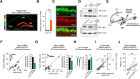
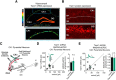
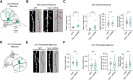
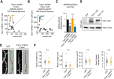
Mounting evidence suggests numerous glutamatergic synapse subtypes exist in the brain, and that these subtypes are likely defined by unique molecular regulatory mechanisms. Recent work has identified substantial divergence of molecular composition between commonly studied Schaffer collateral synapses and perforant path-dentate gyrus (DG) synapses of the hippocampus. However, little is known about the molecular mechanisms that may confer unique properties to perforant path-DG synapses. Here we investigate whether the RhoGEF (Rho guanine-nucleotide exchange factor) protein Tiam1 plays a unique role in the regulation of glutamatergic synapses in dentate granule neurons using a combination of molecular, electrophysiological, and imaging approaches in rat entorhino-hippocampal slices of both sexes. We find that inhibition of Tiam1 function in dentate granule neurons reduces synaptic AMPA receptor function and causes dendritic spines to adopt an elongated filopodia-like morphology. We also find that Tiam1's support of perforant path-DG synapse function is dependent on its GEF domain and identify a potential role for the auto-inhibitory PH domain of Tiam1 in regulating Tiam1 function at these synapses. In marked contrast, reduced Tiam1 expression in CA1 pyramidal neurons produced no effect on glutamatergic synapse development. Together, these data identify a critical role for Tiam1 in the hippocampus and reveal a unique Tiam1-mediated molecular program of glutamatergic synapse regulation in dentate granule neurons.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Several lines of evidence independently point to the molecular diversity of glutamatergic synapses in the brain. Rho guanine-nucleotide exchange factor (RhoGEF) proteins as powerful modulators of glutamatergic synapse function have also become increasingly appreciated in recent years. Here we investigate the synaptic regulatory role of the RhoGEF protein Tiam1, whose expression appears to be remarkably enriched in granule neurons of the dentate gyrus. We find that Tiam1 plays a critical role in the development of glutamatergic perforant path-dentate gyrus synapses, but not in commonly studied in Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses. Together, these data reveal a unique RhoGEF-mediated molecular program of glutamatergic synapse regulation in dentate granule neurons.
Keywords: RhoGEF; Tiam1; dentate gyrus; hippocampus; maturation; synapse.
Copyright © 2019 the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Rac-GEF Tiam1 Promotes Dendrite and Synapse Stabilization of Dentate Granule Cells and Restricts Hippocampal-Dependent Memory Functions.J Neurosci. 2021 Feb 10;41(6):1191-1206. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3271-17.2020. Epub 2020 Dec 16. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33328293 Free PMC article.
-
RhoGEF Tiam2 Regulates Glutamatergic Synaptic Transmission in Hippocampal CA1 Pyramidal Neurons.eNeuro. 2024 Jul 19;11(7):ENEURO.0500-21.2024. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0500-21.2024. Print 2024 Jul. eNeuro. 2024. PMID: 38871458 Free PMC article.
-
Protein 4.1N Plays a Cell Type-Specific Role in Hippocampal Glutamatergic Synapse Regulation.J Neurosci. 2023 Dec 6;43(49):8336-8347. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0185-23.2023. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37845032 Free PMC article.
-
The CA3 "backprojection" to the dentate gyrus.Prog Brain Res. 2007;163:627-37. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(07)63034-9. Prog Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17765742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of cellular mechanisms of long-term depression of synaptic strength at perforant path-granule cell and Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses.Prog Brain Res. 2007;163:473-500. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(07)63026-X. Prog Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17765734 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphoproteome Analysis Identifies a Synaptotagmin-1-Associated Complex Involved in Ischemic Neuron Injury.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2022 May;21(5):100222. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2022.100222. Epub 2022 Mar 5. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2022. PMID: 35257887 Free PMC article.
-
Chr21 protein-protein interactions: enrichment in proteins involved in intellectual disability, autism, and late-onset Alzheimer's disease.Life Sci Alliance. 2022 Aug 1;5(12):e202101205. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202101205. Life Sci Alliance. 2022. PMID: 35914814 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of autism spectrum disorder-related pathogenic trio variants by a novel structure-based approach.Mol Autism. 2024 Apr 3;15(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s13229-024-00590-9. Mol Autism. 2024. PMID: 38566250 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic memory and CaMKII.Physiol Rev. 2023 Oct 1;103(4):2877-2925. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00034.2022. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Physiol Rev. 2023. PMID: 37290118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An optogenetic method for investigating presynaptic molecular regulation.Sci Rep. 2021 May 31;11(1):11329. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90244-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34059719 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
