Decoupling of Nrf2 Expression Promotes Mesenchymal State Maintenance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 31581742
- PMCID: PMC6826656
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11101488
Decoupling of Nrf2 Expression Promotes Mesenchymal State Maintenance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
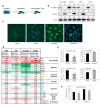
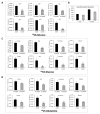
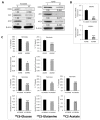
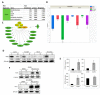
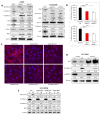
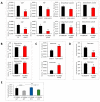
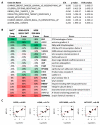
Epithelial mesenchymal transition is a common mechanism leading to metastatic dissemination and cancer progression. In an effort to better understand this process we found an intersection of Nrf2/NLE2F2 (Nrf2), epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), and metabolic alterations using multiple in vitro and in vivo approaches. Nrf2 is a key transcription factor controlling the expression of redox regulators to establish cellular redox homeostasis. Nrf2 has been shown to exert both cancer inhibitory and stimulatory activities. Using multiple isogenic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines, we observed a reduction of Nrf2 protein and activity in a prometastatic mesenchymal cell state and increased reactive oxygen species. Knockdown of Nrf2 promoted a mesenchymal phenotype and reduced glycolytic, TCA cycle and lipogenic output from both glucose and glutamine in the isogenic cell models; while overexpression of Nrf2 promoted a more epithelial phenotype and metabolic reactivation. In both Nrf2 knockout mice and in NSCLC patient samples, Nrf2low was co-correlated with markedly decreased expression of glycolytic, lipogenic, and mesenchymal RNAs. Conversely, Nrf2high was associated with partial mesenchymal epithelial transition and increased expression of metabolic RNAs. The impact of Nrf2 on epithelial and mesenchymal cancer cell states and metabolic output provide an additional context to Nrf2 function in cancer initiation and progression, with implications for therapeutic inhibition of Nrf2 in cancer treatment.
Keywords: Nrf2; TCA cycle; epithelial mesenchymal transition; glycolysis; lipogenesis; redox signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest related to the subject material.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Paracrine IL-6 signaling mediates the effects of pancreatic stellate cells on epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Stat3/Nrf2 pathway in pancreatic cancer cells.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017 Feb;1861(2):296-306. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.10.006. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017. PMID: 27750041
-
Nrf2 activation drive macrophages polarization and cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition during interaction.Cell Commun Signal. 2018 Sep 4;16(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12964-018-0262-x. Cell Commun Signal. 2018. PMID: 30180849 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of long non-coding RNA linc-ITGB1 inhibits cancer stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by reducing the expression of Snail in non-small cell lung cancer.Thorac Cancer. 2019 Feb;10(2):128-136. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12911. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Thorac Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30485693 Free PMC article.
-
ROS-Nrf2 pathway mediates the development of TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the activation of Notch signaling.Eur J Cell Biol. 2021 Sep-Nov;100(7-8):151181. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2021.151181. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Eur J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34763128 Review.
-
Crosstalk between NRF2 and Dicer through metastasis regulating MicroRNAs; mir-34a, mir-200 family and mir-103/107 family.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020 Jun 15;686:108326. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108326. Epub 2020 Mar 3. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020. PMID: 32142889 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative Stress in Cancer.Cancer Cell. 2020 Aug 10;38(2):167-197. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.06.001. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Cancer Cell. 2020. PMID: 32649885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brown fat ATP-citrate lyase links carbohydrate availability to thermogenesis and guards against metabolic stress.Nat Metab. 2024 Nov;6(11):2187-2202. doi: 10.1038/s42255-024-01143-3. Epub 2024 Oct 14. Nat Metab. 2024. PMID: 39402290
-
The Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition at the Crossroads between Metabolism and Tumor Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 12;23(2):800. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020800. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35054987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Reprogramming and Vulnerabilities in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Dec 30;12(1):90. doi: 10.3390/cancers12010090. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31905922 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: The history, regulatory mechanism, and cancer therapeutic opportunities.MedComm (2020). 2022 May 18;3(2):e144. doi: 10.1002/mco2.144. eCollection 2022 Jun. MedComm (2020). 2022. PMID: 35601657 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

