Differential Pathogenicity of SHIV KB9 and 89.6 Env Correlates with Bystander Apoptosis Induction in CD4+ T cells
- PMID: 31581579
- PMCID: PMC6832477
- DOI: 10.3390/v11100911
Differential Pathogenicity of SHIV KB9 and 89.6 Env Correlates with Bystander Apoptosis Induction in CD4+ T cells
Abstract
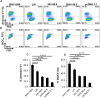
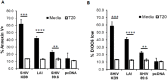
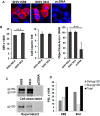
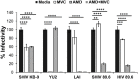
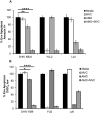
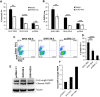
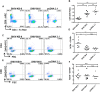
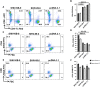
SHIV variants KB9 and 89.6 show differential pathogenesis in primate models with KB9 causing rapid CD4 decline while 89.6 failing to induce disease. We attempted to determine whether the differential pathogenicity of KB9 versus 89.6 was a result of differential bystander apoptosis inducing potential (AIP) of the Env glycoproteins from these viruses. We find that the KB9 Env was highly potent at inducing bystander apoptosis in CD4+ target cells compared to 89.6 Env. Cell death induction by KB9 showed classical signs of apoptosis including mitochondrial depolarization, caspase activation and PARP cleavage. Inhibiting Env mediated fusion by T20 peptide inhibited KB9 mediated bystander apoptosis. KB9 and 89.6 differed in terms of co-receptor usage with 89.6 preferring CXCR4 while KB9 using both CXCR4 and CCR5 with equal efficiency. Our study suggests that higher bystander AIP of KB9 Env compared to 89.6 may be the basis for the differential pathogenesis of these viruses.
Keywords: 89.6; CCR5; CXCR4; Caspase; Envelope; HIV; KB9; SHIV; apoptosis inducing potential; bystander apoptosis; pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Apoptosis of bystander T cells induced by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 with increased envelope/receptor affinity and coreceptor binding site exposure.J Virol. 2004 May;78(9):4541-51. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.9.4541-4551.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15078935 Free PMC article.
-
Simian-human immunodeficiency virus containing a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype-E envelope gene: persistent infection, CD4(+) T-cell depletion, and mucosal membrane transmission in macaques.J Virol. 2000 Sep;74(17):7851-60. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.17.7851-7860.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10933692 Free PMC article.
-
HIV envelope proteins differentially utilize CXCR4 and CCR5 coreceptors for induction of apoptosis.Virology. 2001 Jun 20;285(1):128-37. doi: 10.1006/viro.2001.0927. Virology. 2001. PMID: 11414813
-
Understanding the basis of CD4(+) T-cell depletion in macaques infected by a simian-human immunodeficiency virus.Vaccine. 2002 May 6;20(15):1934-7. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(02)00072-5. Vaccine. 2002. PMID: 11983249 Review.
-
Autophagy and CD4+ T lymphocyte destruction by HIV-1.Autophagy. 2007 Jan-Feb;3(1):32-4. doi: 10.4161/auto.3275. Epub 2007 Jan 14. Autophagy. 2007. PMID: 17012832 Review.
References
-
- Silvestri G., Sodora D.L., Koup R.A., Paiardini M., O’Neil S.P., McClure H.M., Staprans S.I., Feinberg M.B. Nonpathogenic SIV infection of sooty mangabeys is characterized by limited bystander immunopathology despite chronic high-level viremia. Immunity. 2003;18:441–452. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(03)00060-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

