Correlation analysis of expression and prognosis of TTF-1 and CD44v6 in undifferentiated lung carcinoma
- PMID: 31579090
- PMCID: PMC6757272
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2019.10689
Correlation analysis of expression and prognosis of TTF-1 and CD44v6 in undifferentiated lung carcinoma
Abstract
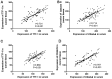
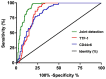
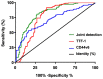
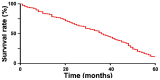
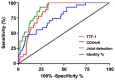
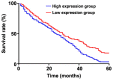
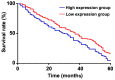
The correlation between expression and prognosis of thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1) and CD44v6 in undifferentiated lung carcinoma was investigated. There were 116 cases with large cell undifferentiated carcinoma in group A, 120 cases with small cell undifferentiated carcinoma in group B and 80 normal individuals from the same period in group C. The expression levels of TTF-1 and CD44v6 in the serum of group A, B and C and the cancer tissues and adjacent tissues of group A, B and C were detected using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and the levels in each group were compared. Pearsons test was used to analyze the correlation between TTF-1 and CD44v6 expression in serum of group A and group B and cancer tissues. Patients were divided into the survival group and the deceased group according to their 5-year survival. Multivariate logistic regression was applied to analyze the risk factors of mortality, and receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) was used to analyze the diagnostic value of TTF-1 and CD44v6. The best cut-off values of TTF-1 and CD44v6 were divided into the high and low expression groups to observe the 5-year mortality of patients and the Kaplan-Meier (K-M) survival curve was drawn. Multivariate logistic regression was used to analyze the risk factors of mortality. The expression of CD44v6 in the serum of group A and group B was higher than that in group C, and that of group B was higher than that in group A (P<0.05). The expression of TTF-1 in serum of group A and group B was higher than that of group C, and the expression of TTF-1 in group A was higher than that in group B (P<0.05). The expression of TTF-1 and CD44v6 in group A and group B were significantly higher than those in adjacent tissues (P<0.05). The expression of TTF-1 in group A was higher than that in group B (P<0.05), and that of CD44v6 was lower than that in group B (P<0.05). The 5-year survival of patients showed that 209 patients died and 27 survived at 5 years; the survival rate was 11.44%. The course of disease, TNM stage, TTF-1 and CD44v6 were independent mortality factors for undifferentiated lung cancer.
Keywords: CD44v6; TTF-1; large cell undifferentiated carcinoma; small cell undifferentiated carcinoma; undifferentiated lung carcinoma.
Copyright: © Wu et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cytokeratin 7 and thyroid transcription factor - 1 levels in patients with lung cancer complicated with superior vena cava syndrome and their correlation with clinicopathological characteristics.J BUON. 2019 Nov-Dec;24(6):2294-2302. J BUON. 2019. PMID: 31983097
-
[Variation of serum thyroid transcription factor-1 protein and its value in the diagnosis of lung carcinoma].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2011 Sep;31(9):1592-6. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2011. PMID: 21945775 Chinese.
-
[Thyroid transcription factor-1 level is associated with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2014 Dec;37(12):919-23. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25609130 Chinese.
-
Value of circulating tumor cells positive for thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1) to predict recurrence and survival rates for endometrial carcinoma.J BUON. 2016 Nov-Dec;21(6):1491-1495. J BUON. 2016. PMID: 28039713
-
[Expression of CD44V6 in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2001 Oct 20;4(5):367-70. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2001.05.15. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2001. PMID: 21059320 Chinese.
References
-
- Aristarco V, Serrano D, Gandini S, Johansson H, Macis D, Guerrieri-Gonzaga A, Lazzeroni M, Feroce I, Pruneri G, Pagani G, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled, phase II, presurgical biomarker trial of celecoxib versus exemestane in postmenopausal breast cancer patients. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2016;9:349–356. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-15-0311. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rudin CM, Ismaila N, Hann CL, Malhotra N, Movsas B, Norris K, Pietanza MC, Ramalingam SS, Turrisi AT, III, Giaccone G. Treatment of small-cell lung cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians Guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:4106–4111. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.63.7918. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
