Comparative analysis of the catalytic regulation of NEDD4-1 and WWP2 ubiquitin ligases
- PMID: 31578285
- PMCID: PMC6873185
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009211
Comparative analysis of the catalytic regulation of NEDD4-1 and WWP2 ubiquitin ligases
Abstract
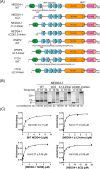
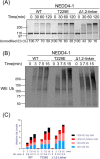
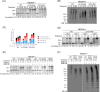
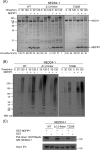
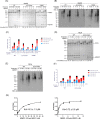
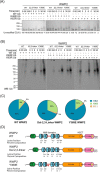
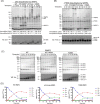
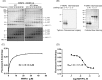
NEDD4-1 E3 ubiquitin protein ligase (NEDD4-1) and WW domain-containing E3 ubiquitin ligase (WWP2) are HECT family ubiquitin E3 ligases. They catalyze Lys ubiquitination of themselves and other proteins and are important in cell growth and differentiation. Regulation of NEDD4-1 and WWP2 catalytic activities is important for controlling cellular protein homeostasis, and their dysregulation may lead to cancer and other diseases. Previous work has implicated noncatalytic regions, including the C2 domain and/or WW domain linkers in NEDD4-1 and WWP2, in contributing to autoinhibition of the catalytic HECT domains by intramolecular interactions. Here, we explored the molecular mechanisms of these NEDD4-1 and WWP2 regulatory regions and their interplay with allosteric binding proteins such as Nedd4 family-interacting protein (NDFIP1), engineered ubiquitin variants, and linker phosphomimics. We found that in addition to influencing catalytic activities, the WW domain linker regions in NEDD4-1 and WWP2 can impact product distribution, including the degree of polyubiquitination and Lys-48 versus Lys-63 linkages. We show that allosteric activation by NDFIP1 or engineered ubiquitin variants is largely mediated by relief of WW domain linker autoinhibition. WWP2-mediated ubiquitination of WW domain-binding protein 2 (WBP2), phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), and p62 proteins by WWP2 suggests that substrate ubiquitination can also be influenced by WW linker autoinhibition, although to differing extents. Overall, our results provide a deeper understanding of the intricate and multifaceted set of regulatory mechanisms in the control of NEDD4-1-related ubiquitin ligases.
Keywords: E3 ubiquitin ligase; NEDD4 E3 ubiquitin protein ligase (NEDD4); Nedd4 family interaction protein (Ndfip1); WW domain-binding protein 2 (WBP2); WW domain-containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 2 (WWP2); allosteric regulation; enzyme; enzyme homeostasis; post-translational modification (PTM); ubiquitin.
© 2019 Jiang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
Similar articles
-
Itch WW Domains Inhibit Its E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Activity by Blocking E2-E3 Ligase Trans-thiolation.J Biol Chem. 2015 Sep 25;290(39):23875-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.649269. Epub 2015 Aug 5. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26245901 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric auto-inhibition and activation of the Nedd4 family E3 ligase Itch.EMBO Rep. 2017 Sep;18(9):1618-1630. doi: 10.15252/embr.201744454. Epub 2017 Jul 26. EMBO Rep. 2017. PMID: 28747490 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the divalent metal ion transporter DMT1 and iron homeostasis by a ubiquitin-dependent mechanism involving Ndfips and WWP2.Blood. 2008 Nov 15;112(10):4268-75. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-04-150953. Epub 2008 Sep 5. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18776082
-
Physiological Functions of the Ubiquitin Ligases Nedd4-1 and Nedd4-2.Physiology (Bethesda). 2024 Jan 1;39(1):18-29. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00023.2023. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Physiology (Bethesda). 2024. PMID: 37962894 Review.
-
The role of Nedd4/Nedd4-like dependant ubiquitylation in epithelial transport processes.Pflugers Arch. 2003 Jun;446(3):334-8. doi: 10.1007/s00424-003-1027-x. Epub 2003 Apr 16. Pflugers Arch. 2003. PMID: 12698368 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein semisynthesis reveals plasticity in HECT E3 ubiquitin ligase mechanisms.Nat Chem. 2024 Nov;16(11):1894-1905. doi: 10.1038/s41557-024-01576-z. Epub 2024 Jul 19. Nat Chem. 2024. PMID: 39030419
-
WW domain binding protein 2 (WBP2) as an oncogene in breast cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic prospects-a narrative review.Gland Surg. 2022 Dec;11(12):1984-2002. doi: 10.21037/gs-22-716. Gland Surg. 2022. PMID: 36654949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting PY motif-mediated protein-protein interactions in the Nedd4 family of ubiquitin ligases.PLoS One. 2021 Oct 12;16(10):e0258315. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258315. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34637467 Free PMC article.
-
Enzymatic analysis of WWP2 E3 ubiquitin ligase using protein microarrays identifies autophagy-related substrates.J Biol Chem. 2022 May;298(5):101854. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101854. Epub 2022 Mar 21. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35331737 Free PMC article.
-
The Ubiquitin Proteasome System and Skin Fibrosis.Mol Diagn Ther. 2021 Jan;25(1):29-40. doi: 10.1007/s40291-020-00509-z. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Mol Diagn Ther. 2021. PMID: 33433895 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

