Benefit effect of REM-sleep deprivation on memory impairment induced by intensive exercise in male wistar rats: with respect to hippocampal BDNF and TrkB
- PMID: 31576186
- PMCID: PMC6767759
- DOI: 10.2147/NSS.S207339
Benefit effect of REM-sleep deprivation on memory impairment induced by intensive exercise in male wistar rats: with respect to hippocampal BDNF and TrkB
Abstract
Background: Many factors affect our learning and memory quality, but according to different studies, having a positive or negative impact pertains to their characteristics like intensity or the amount.
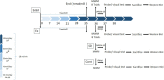
Purpose: The present study was conducted to investigate the effect of 24-hour REM-sleep deprivation on continuous-high intensity forced exercise-induced memory impairment and its effect on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and Tyrosine kinase B (TrkB) levels in the hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex area (PFC).
Material and methods: Animals were conditioned to run on treadmills for 5 weeks then, were deprived of sleep for 24 h using the modified multiple platforms. The effect of intensive exercise and/or 24-h REM-SD was studied on behavioral performance using Morris Water Maze protocol for 2 days, and BDNF/TrkB levels were assessed in hippocampus and PFC after behavioral probe test using western blotting.
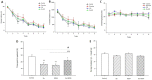
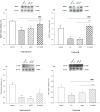
Results: After 5 weeks of intensive exercise and 24-h REM-SD, spatial memory impairment and reduction of BDNF and TrkB levels were found in hippocampus and PFC. 24-h REM-SD improved memory impairment and intensive exercise-induced downregulation of BDNF and TrkB protein levels.
Conclusion: The results of the study suggested that sleep deprivation might act as a compensatory factor to reduce memory impairment when the animal is under severe stressful condition.
Keywords: BDNF; TrkB; hippocampus; intensive exercise; prefrontal cortex; sleep deprivation; spatial memory.
© 2019 Mahboubi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Electroacupuncture promotes the survival and synaptic plasticity of hippocampal neurons and improvement of sleep deprivation-induced spatial memory impairment.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021 Dec;27(12):1472-1482. doi: 10.1111/cns.13722. Epub 2021 Oct 8. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021. PMID: 34623740 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the effect of crocin on memory deficits induced by total sleep deprivation (TSD) with respect to the BDNF, TrkB and ERK levels in the hippocampus of male Wistar rats.J Psychopharmacol. 2021 Jun;35(6):744-754. doi: 10.1177/02698811211000762. Epub 2021 Apr 25. J Psychopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33899577
-
Regular exercise prevents sleep deprivation associated impairment of long-term memory and synaptic plasticity in the CA1 area of the hippocampus.Sleep. 2013 May 1;36(5):751-61. doi: 10.5665/sleep.2642. Sleep. 2013. PMID: 23633758 Free PMC article.
-
The Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor: Missing Link Between Sleep Deprivation, Insomnia, and Depression.Neurochem Res. 2020 Feb;45(2):221-231. doi: 10.1007/s11064-019-02914-1. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Neurochem Res. 2020. PMID: 31782101 Review.
-
Interaction of BDNF/TrkB signaling with NMDA receptor in learning and memory.Drug News Perspect. 2004 Sep;17(7):435-8. doi: 10.1358/dnp.2004.17.7.863702. Drug News Perspect. 2004. PMID: 15514702 Review.
Cited by
-
Low-Dose Ozone Therapy Improves Sleep Quality in Patients with Insomnia and Coronary Heart Disease by Elevating Serum BDNF and GABA.Bull Exp Biol Med. 2021 Feb;170(4):493-498. doi: 10.1007/s10517-021-05095-6. Epub 2021 Mar 13. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33713235
-
Complicated Role of Exercise in Modulating Memory: A Discussion of the Mechanisms Involved.Neurochem Res. 2022 Jun;47(6):1477-1490. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03552-w. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Neurochem Res. 2022. PMID: 35195832 Review.
-
The role of sleep deprivation in streptozotocin-induced Alzheimer's disease-like sporadic dementia in rats with respect to the serum level of oxidative and inflammatory markers.Exp Brain Res. 2022 Dec;240(12):3259-3270. doi: 10.1007/s00221-022-06471-y. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Exp Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 36301335
-
Butanol Extract of Tinospora cordifolia Alleviates Acute Sleep Deprivation-Induced Impairments in Cognitive Functions and Neuromuscular Coordination in Middle-Aged Female Rats.Neuromolecular Med. 2022 Jun;24(2):202-214. doi: 10.1007/s12017-021-08683-x. Epub 2021 Aug 19. Neuromolecular Med. 2022. PMID: 34410631
-
REM Sleep Deprivation Impairs Learning and Memory by Decreasing Brain O-GlcNAc Cycling in Mouse.Neurotherapeutics. 2021 Oct;18(4):2504-2517. doi: 10.1007/s13311-021-01094-7. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Neurotherapeutics. 2021. PMID: 34312767 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguiar A Jr, Pinho R. The brain redox paradox of physical exercise In: Kozyrev D, Slutsky V, editors. Handbook of Free Radicals: Formation, Types and Effects. New York: Nova Science Publishers Company; 2010:153–166.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

