Tuning the surface coating of IONs toward efficient sonochemical tethering and sustained liberation of topoisomerase II poisons
- PMID: 31571866
- PMCID: PMC6756273
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S208810
Tuning the surface coating of IONs toward efficient sonochemical tethering and sustained liberation of topoisomerase II poisons
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Tuning the Surface Coating of IONs Toward Efficient Sonochemical Tethering and Sustained Liberation of Topoisomerase II Poisons [Corrigendum].Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Mar 1;16:1707-1708. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S307422. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33688186 Free PMC article.
Abstract
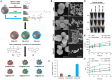
Background: Iron oxide nanoparticles (IONs) have been increasingly utilized in a wide spectrum of biomedical applications. Surface coatings of IONs can bestow a number of exceptional properties, including enhanced stability of IONs, increased loading of drugs or their controlled release.
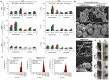
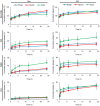
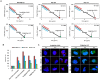
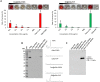
Methods: Using two-step sonochemical protocol, IONs were surface-coated with polyoxyethylene stearate, polyvinylpyrrolidone or chitosan for a loading of two distinct topo II poisons (doxorubicin and ellipticine). The cytotoxic behavior was tested in vitro against breast cancer (MDA-MB-231) and healthy epithelial cells (HEK-293 and HBL-100). In addition, biocompatibility studies (hemotoxicity, protein corona formation, binding of third complement component) were performed.
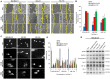
Results: Notably, despite surface-coated IONs exhibited only negligible cytotoxicity, upon tethering with topo II poisons, synergistic or additional enhancement of cytotoxicity was found in MDA-MB-231 cells. Pronounced anti-migratory activity, DNA fragmentation, decrease in expression of procaspase-3 and enhancement of p53 expression were further identified upon exposure to surface-coated IONs with tethered doxorubicin and ellipticine. Moreover, surface-coated IONs nanoformulations of topo II poisons exhibited exceptional stability in human plasma with no protein corona and complement 3 binding, and only a mild induction of hemolysis in human red blood cells.
Conclusion: The results imply a high potential of an efficient ultrasound-mediated surface functionalization of IONs as delivery vehicles to improve therapeutic efficiency of topo II poisons.
Keywords: doxorubicin; ellipticine; iron oxide; nanoparticles; release kinetics.
© 2019 Michalkova et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nitric oxide inhibits topoisomerase II activity and induces resistance to topoisomerase II-poisons in human tumor cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jul;1860(7):1519-27. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.04.009. Epub 2016 Apr 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 27095671 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage response (DDR) induced by topoisomerase II poisons requires nuclear function of the small GTPase Rac.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1833(12):3093-3103. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.08.016. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23999236
-
Rac1 protein signaling is required for DNA damage response stimulated by topoisomerase II poisons.J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 9;287(46):38590-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.377903. Epub 2012 Sep 25. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23012366 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Novel Topoisomerase II Inhibitors by Medicinal Chemistry Approaches.J Med Chem. 2018 Oct 25;61(20):8947-8980. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01202. Epub 2018 Jun 20. J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29870668 Review.
-
Recent advances in the development of dual topoisomerase I and II inhibitors as anticancer drugs.Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(35):4270-90. doi: 10.2174/092986710793361252. Curr Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20939813 Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the nanotoxicological aspects of Se nanomaterials differing in size and morphology.Bioact Mater. 2022 Jun 25;20:489-500. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.06.014. eCollection 2023 Feb. Bioact Mater. 2022. PMID: 35800405 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

