Correlation between 18F-FDG maximum standardized uptake value with CD147 expression in lung adenocarcinomas: a retrospective study
- PMID: 31565568
- PMCID: PMC6741284
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.7635
Correlation between 18F-FDG maximum standardized uptake value with CD147 expression in lung adenocarcinomas: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: The pro-tumoral action of the cluster of differentiation 147 (CD147), which is associated with the chemotherapy resistance of lung adenocarcinoma, is partly due to accelerated tumor cell glycolysis. 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (18F-FDG PET) metabolic parameters included maximal standardized uptake value (SUVmax), mean standardized uptake value (SUVmean), metabolic tumor volume (MTV), and total lesion glycolysis (TLG), which are non-invasive markers of the glucose metabolism of tumor cells in vivo. This study aimed to clarify the correlation between PET metabolic parameters and CD147 expression, and to evaluate the prognostic value of CD147 expression in resectable lung adenocarcinoma patients.
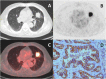
Methods: A total of 89 lung adenocarcinoma chemotherapy-naive patients who underwent 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and computerized tomography scan before pulmonary surgery were retrospectively analyzed. The PET metabolic parameters were calculated by 18F-FDG PET imaging, and CD147 expression was analyzed by immunohistochemistry. SUVmax, SUVmean, MTV, and TLG compared for their performance in predicting the expression of CD147 were illustrated with statistical analysis. All patients were then followed-up for survival analysis.
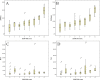
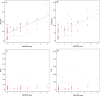
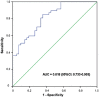
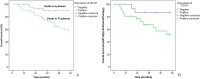
Results: The SUVmax was significantly correlated with the CD147 expression and was the primary predictor for the CD147 expression of lung adenocarcinoma. A cut-off value of the SUVmax, 9.77 allowed 85.1% sensitivity and 64.3% specificity for predicting the CD147 positive lung adenocarcinoma. CD147 expression was correlated with tumor differentiation and metastasis. Univariate survival analysis showed that CD147 expression was significantly associated with a shorter overall survival (OS) time. Multivariate analysis revealed that CD147 was an independent prognostic factor of lung adenocarcinoma patients.
Conclusion: The SUVmax of a primary tumor measured with 18F-FDG PET may be a simple and non-invasive marker for predicting CD147 expression in lung adenocarcinoma. CD147 is an independent prognostic factor related to OS of postoperative lung adenocarcinoma patients.
Keywords: 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (18F-FDG PET); Chemotherapy resistance; Cluster of differentiation 147 (CD147); Lung adenocarcinoma; Maximal standardized uptake values (SUVmax).
© 2019 Guo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nucleophosmin 1 overexpression correlates with 18F-FDG PET/CT metabolic parameters and improves diagnostic accuracy in patients with lung adenocarcinoma.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021 Mar;48(3):904-912. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-05005-4. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021. PMID: 32856112
-
Lymph node standardized uptake values at pre-treatment 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography as a valuable prognostic factor for distant metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Br J Radiol. 2017 Mar;90(1071):20160239. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20160239. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Br J Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28008776 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of Metabolic Tumor Volume and Total Lesion Glycolysis on Preoperative ¹⁸F-FDG PET/CT in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer.J Nucl Med. 2014 Jun;55(6):898-904. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.113.131847. Epub 2014 Apr 7. J Nucl Med. 2014. PMID: 24711649
-
Prognostic Value of Metabolic and Volumetric Parameters of Preoperative FDG-PET/CT in Patients With Resectable Pancreatic Cancer.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 May;95(19):e3686. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003686. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27175707 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced glucose metabolism mediated by CD147 is associated with 18 F-FDG PET/CT imaging in lung adenocarcinoma.Thorac Cancer. 2020 May;11(5):1245-1257. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13383. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32162491 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

