Structure and Dynamics of Mono- vs. Doubly Lipidated Rab5 in Membranes
- PMID: 31561436
- PMCID: PMC6801778
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20194773
Structure and Dynamics of Mono- vs. Doubly Lipidated Rab5 in Membranes
Abstract
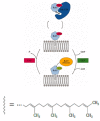
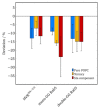
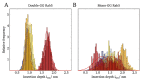
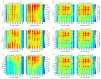
The Rab5 small GTPase is a regulator of endosomal trafficking and vesicle fusion. It possesses two adjacent cysteine residues for post-translational geranylgeranylation at its C-terminus for the protein to associate with the early endosome membrane. We compare the effect of mono-lipidification of only one cysteine residue with the doubly modified, fully functional Rab protein in both guanosine diphosphate (GDP)- and guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-bound states and in different membranes (one, three, and six-component membranes). Molecular simulations show that the mono-geranylgeranylated protein is less strongly associated with the membranes and diffuses faster than the doubly lipidated protein. The geranylgeranyl anchor membrane insertion depth is smaller and the protein-membrane distance distribution is broad and uncharacteristic for the membrane composition. The mono-geranylgeranylated protein reveals an unspecific association with the membrane and an orientation at the membrane that does not allow a nucleotide-specific recruitment of further effector proteins. This work shows that double-lipidification is critical for Rab5 to perform its physiological function and mono-geranylgeranylation renders it membrane-associated but non-functional.
Keywords: GTPase; diffusion; lipid bilayer; molecular dynamics; post-translation modification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Membrane localization and dynamics of geranylgeranylated Rab5 hypervariable region.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2017 Aug;1859(8):1335-1349. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2017.04.021. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2017. PMID: 28455099
-
Recognition and stabilization of geranylgeranylated human Rab5 by the GDP Dissociation Inhibitor (GDI).Small GTPases. 2019 May;10(3):227-242. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2017.1371268. Epub 2017 Oct 25. Small GTPases. 2019. PMID: 29065764 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the druggability of membrane-bound Rab5 by molecular dynamics simulations.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2017 Dec;32(1):434-443. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2016.1260564. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28090783 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenesis of the sorting endosome: the role of Rab5.Traffic. 2000 Sep;1(9):695-701. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2000.010902.x. Traffic. 2000. PMID: 11208157 Review.
-
Membrane recruitment of effector proteins by Arf and Rab GTPases.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005 Dec;15(6):681-9. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2005.10.015. Epub 2005 Nov 9. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005. PMID: 16289847 Review.
Cited by
-
Treatment of a mutant KRAS lung cancer cell line with polyisoprenylated cysteinyl amide inhibitors activates the MAPK pathway, inhibits cell migration and induces apoptosis.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 22;19(10):e0312563. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312563. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39436906 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Lipid-Modified Signaling Proteins.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2315:141-159. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1468-6_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34302675 Free PMC article.
-
A non-linear system patterns Rab5 GTPase on the membrane.Elife. 2020 Jun 8;9:e54434. doi: 10.7554/eLife.54434. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32510320 Free PMC article.
-
Polyisoprenylated cysteinyl amide inhibitors deplete singly polyisoprenylated monomeric G-proteins in lung and breast cancer cell lines.Oncotarget. 2023 Mar 24;14:243-257. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28390. Oncotarget. 2023. PMID: 36961909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li G.P., Stahl P.D. Structure-function relationship of the small GTPase Rab5. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:24475–24480. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

