Identification of inflammatory markers suitable for non-invasive, repeated measurement studies in biobehavioral research: A feasibility study
- PMID: 31550260
- PMCID: PMC6759186
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221993
Identification of inflammatory markers suitable for non-invasive, repeated measurement studies in biobehavioral research: A feasibility study
Abstract
Introduction: Studying the role of the immune system in the interaction between mental and physical health is challenging. To study individuals with an intensive, longitudinal study design that requires repetitive sampling in their daily life, non-invasive sampling techniques are a necessity. Urine can be collected in a non-invasive way, but this may be demanding for participants and little is known about fluctuation of inflammatory markers in urine over time. The aim of this study was to investigate the feasibility of non-invasive sampling, and to explore intra-individual differences in inflammatory markers in urine.
Materials & methods: Ten healthy individuals collected 24-hour urine for 63 consecutive days. In a pilot analysis, 39 inflammatory markers were examined for detectability in urine, stability over time and under storage conditions, and daily fluctuations. Multiplex analyses were used to quantify levels of eight selected markers: C-reactive protein (CRP), Fractalkine, Interleukin-1 receptor-antagonist (IL-1RA), interferon-α (IFNα), interferon-γ (IFNγ), Interferon gamma-induced protein 10 (IP10), Macrophage inflammatory protein-1β (MIP-1β), and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF). Cross-correlations were calculated between the overnight and 24-hour samples were calculated, to examine whether 24-hour urine could be replaced by the overnight portion for better feasibility. We examined intra- and interindividual differences in the levels of inflammatory markers in urine and the fluctuations thereof.
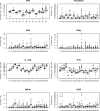
Results: This study showed that levels of selected inflammatory markers can be detected in urine. Cross-correlation analyses showed that correlations between levels of inflammatory markers in the night portion and the 24-hour urine sample varied widely between individuals. In addition, analyses of time series revealed striking inter- and intra-individual variation in levels of inflammatory markers and their fluctuations.
Conclusion: We show that the assessment of urinary inflammatory markers is feasible in an intensive day-to-day study in healthy individuals. However, 24-hour urine cannot be replaced by an overnight portion to alleviate the protocol burden. Levels of inflammatory markers show substantial variation between and within persons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expressions of mRNA for innate immunity-associated functional molecules in urinary sediment in immunoglobulin A nephropathy.Nephrology (Carlton). 2015 Dec;20(12):916-21. doi: 10.1111/nep.12533. Nephrology (Carlton). 2015. PMID: 26058859
-
Early Detection of Pressure Ulcer Development Following Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury Using Inflammatory Mediators.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2016 Oct;97(10):1656-62. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2016.01.003. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2016. PMID: 26820323
-
Soluble TNF-R1, VEGF and other cytokines as markers of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis.Lupus. 2019 May;28(6):713-721. doi: 10.1177/0961203319845487. Epub 2019 May 2. Lupus. 2019. PMID: 31046570
-
Associations of Self-Reported Sleep Quality with Circulating Interferon Gamma-Inducible Protein 10, Interleukin 6, and High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein in Healthy Menopausal Women.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 6;12(1):e0169216. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169216. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28060925 Free PMC article.
-
Studying Within-Person Variation and Within-Person Couplings in Intensive Longitudinal Data: Lessons Learned and to Be Learned.Gerontology. 2020;66(4):332-339. doi: 10.1159/000507993. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Gerontology. 2020. PMID: 32526756 Review.
Cited by
-
Innate immunity impacts social-cognitive functioning in people with multiple sclerosis and healthy individuals: Implications for IL-1ra and urinary immune markers.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2021 Apr 14;14:100254. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2021.100254. eCollection 2021 Jul. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2021. PMID: 34589763 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers of Stress and Inflammation in Children.Biol Res Nurs. 2023 Oct;25(4):559-570. doi: 10.1177/10998004231168805. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Biol Res Nurs. 2023. PMID: 37010976 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

