Increased expression of miR-601 is associated with poor prognosis and tumor progression of gastric cancer
- PMID: 31547835
- PMCID: PMC6757374
- DOI: 10.1186/s13000-019-0882-5
Increased expression of miR-601 is associated with poor prognosis and tumor progression of gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been considered to participate in many tumorigenesis, including gastric cancer (GC). Abnormal expression of miR-601 has been reported in GC, but its role is not clear. The goal of this study is to explore the expression patterns, clinical value and functional role of miR-601 in GC.
Methods: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was conducted to evaluate the expression level of miR-601. The association between miR-601 expression and overall survival was estimated by the Kaplan-Meier survival method. The significance of different variables with respect to survival was analyzed by using the Cox regression assay. Cell experiments were applied to investigate the functional role of miR-601 in GC.
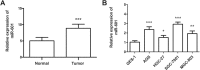
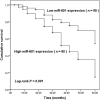
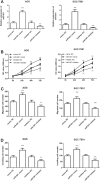
Results: We found that miR-601 was significantly up-regulated in GC tissues and cells compared with the controls (all P < 0.01). The levels of miR-601 expression were significantly associated with TNM stage, lymph node metastasis, lymphatic invasion, and distant metastasis (all P < 0.05). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that patients in the high miR-601 expression group had poor overall survival (log-rank P = 0.001). Moreover, we confirmed that miR-601, TNM stage, and distant metastasis were independent prognostic factors for GC patients. Overexpression of miR-601 in AGS and SGC-7901 cells by miR-601 mimic transfection significantly promoted the cell proliferation, migration, and invasion (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: The expression level of miR-601 is dramatically up-regulated in GC. The overexpression of miR-601 promotes the tumor progression of GC, and may be a novel prognostic factor for poor survival in GC patients.
Keywords: Gastric cancer; MicroRNA-601; Prognosis; Progression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased expression of miR-181d is associated with poor prognosis and tumor progression of gastric cancer.Cancer Biomark. 2019;26(3):353-360. doi: 10.3233/CBM-190091. Cancer Biomark. 2019. PMID: 31524144
-
MiR-652 serves as a prognostic biomarker in gastric cancer and promotes tumor proliferation, migration, and invasion via targeting RORA.Cancer Biomark. 2019;26(3):323-331. doi: 10.3233/CBM-190361. Cancer Biomark. 2019. PMID: 31524147
-
Upregulation of miR-552 Predicts Unfavorable Prognosis of Gastric Cancer and Promotes the Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Gastric Cancer Cells.Oncol Res Treat. 2020;43(3):103-111. doi: 10.1159/000505377. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Oncol Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 31958799
-
Prognostic role of microRNA-21 in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis.Med Sci Monit. 2014 Sep 18;20:1668-74. doi: 10.12659/MSM.892096. Med Sci Monit. 2014. PMID: 25230738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Biomarkers of microRNAs in Gastric Cancer: An Overview from Diagnosis to Treatment.Microrna. 2022;11(1):12-24. doi: 10.2174/2211536611666220322160242. Microrna. 2022. PMID: 35319404 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of microRNAs in the gastric cancer tumor microenvironment.Mol Cancer. 2024 Aug 20;23(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02084-x. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39164671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-3196 acts as a Tumor Suppressor and Predicts Survival Outcomes in Patients With Gastric Cancer.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1533033820923427. doi: 10.1177/1533033820923427. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 32419651 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA in Gastric Cancer Development: Mechanisms and Biomarkers.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Oct 31;10(11):891. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10110891. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33142817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of miRNA-601 and PD-L1 among Iranian Patients with Lung Cancer and Their Relationship with Smoking and Mycoplasma Infection.Cell J. 2021 Dec;23(7):723-729. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2021.7704. Epub 2021 Dec 29. Cell J. 2021. PMID: 34979060 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of miR-484 is associated with poor prognosis and tumor progression of gastric cancer.Diagn Pathol. 2020 Mar 20;15(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s13000-020-00946-8. Diagn Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32192507 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

