HMGB1-triggered inflammation inhibition of notoginseng leaf triterpenes against cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury via MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways
- PMID: 31547018
- PMCID: PMC6843331
- DOI: 10.3390/biom9100512
HMGB1-triggered inflammation inhibition of notoginseng leaf triterpenes against cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury via MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways
Abstract
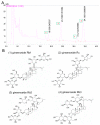
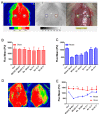
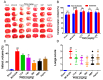
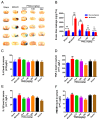
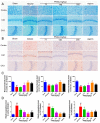
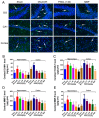
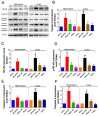
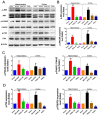
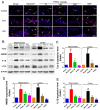
Ischemic stroke is a clinically common cerebrovascular disease whose main risks include necrosis, apoptosis and cerebral infarction, all caused by cerebral ischemia and reperfusion (I/R) injury. This process has particular significance for the treatment of stroke patients. Notoginseng leaf triterpenes (PNGL), as a valuable medicine, have been discovered to have neuroprotective effects. However, it was not confirmed that whether PNGL may possess neuroprotective effects against cerebral I/R injury. To explore the neuroprotective effects of PNGL and their underlying mechanisms, a middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion (MCAO/R) model was established. In vivo results suggested that in MCAO/R model rats, PNGL pretreatment (73.0, 146, 292 mg/kg) remarkably decreased infarct volume, reduced brain water content, and improved neurological functions; moreover, PNGL (73.0, 146, 292 mg/kg) significantly alleviated blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption and inhibited neuronal apoptosis and neuronal loss caused by cerebral I/R injury, while PNGL with a different concertation (146, 292 mg/kg) significantly reduced the concentrations of IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1 β, and HMGB1 in serums in a dose-dependent way, which indicated that inflammation inhibition could be involved in the neuroprotective effects of PNGL. The immunofluorescence and western blot analysis showed PNGL decreased HMGB1 expression, suppressed the HMGB1-triggered inflammation, and inhibited microglia activation (IBA1) in hippocampus and cortex, thus dose-dependently downregulating inflammatory cytokines including VCAM-1, MMP-9, MMP-2, and ICAM-1 concentrations in ischemic brains. Interestingly, PNGL administration (146 mg/kg) significantly downregulated the levels of p-P44/42, p-JNK1/2 and p-P38 MAPK, and also inhibited expressions of the total NF-κB and phosphorylated NF-κB in ischemic brains, which was the downstream pathway triggered by HMGB1. All of these results indicated that the protective effects of PNGL against cerebral I/R injury could be associated with inhibiting HMGB1-triggered inflammation, suppressing the activation of MAPKs and NF-κB, and thus improved cerebral I/R-induced neuropathological changes. This study may offer insight into discovering new active compounds for the treatment of ischemic stroke.
Keywords: HMGB1; MAPK; NF-κB; cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury; inflammation; notoginseng leaf triterpenes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Notoginseng leaf triterpenes promotes angiogenesis by activating the Nrf2 pathway and AMPK/SIRT1-mediated PGC-1/ERα axis in ischemic stroke.Fitoterapia. 2024 Jul;176:106045. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2024.106045. Epub 2024 May 31. Fitoterapia. 2024. PMID: 38823597
-
Notoginseng Leaf Triterpenes Ameliorates OGD/R-Induced Neuronal Injury via SIRT1/2/3-Foxo3a-MnSOD/PGC-1α Signaling Pathways Mediated by the NAMPT-NAD Pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Oct 23;2020:7308386. doi: 10.1155/2020/7308386. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 33149812 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the Combination of the Main Active Components of Astragalus and Panax notoginseng on Inflammation and Apoptosis of Nerve Cell after Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion.Am J Chin Med. 2015;43(7):1419-38. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X15500809. Epub 2015 Oct 18. Am J Chin Med. 2015. PMID: 26477799
-
Loureirin B protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through modulating M1/M2 microglial polarization via STAT6 / NF-kappaB signaling pathway.Eur J Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 15;953:175860. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175860. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37331681 Review.
-
Downregulation of Nogo-B ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice through regulating microglia polarization via TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway.Neurochem Int. 2023 Jul;167:105553. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2023.105553. Epub 2023 May 23. Neurochem Int. 2023. PMID: 37230196 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of notoginseng leaf triterpenes on small molecule metabolism after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury assessed using MALDI-MS imaging.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Feb;9(3):246. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-4898. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33708873 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytic CD24 Protects Neuron from Recombinant High-Mobility Group Box 1 Protein(rHMGB1)-Elicited Neuronal Injury.Brain Sci. 2022 Aug 23;12(9):1119. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12091119. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 36138855 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of Gypenoside XVII against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via SIRT1-FOXO3A- and Hif1a-BNIP3-mediated mitochondrial autophagy.J Transl Med. 2022 Dec 27;20(1):622. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03830-9. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36572901 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Observation of Salvianolic Acid Combined with Panax Notoginseng Saponins Combined with Basic Nursing Intervention on Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Jan 30;2022:8706730. doi: 10.1155/2022/8706730. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. PMID: 35136538 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-apoptosis effect of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury.Apoptosis. 2023 Jun;28(5-6):702-729. doi: 10.1007/s10495-023-01824-6. Epub 2023 Mar 9. Apoptosis. 2023. PMID: 36892639 Review.
References
-
- Jamison J.T. Dissertations Theses. Wayne State University; Detroit, MI, USA: Jan, 2011. Mechanisms of persistent translation arrest following global brain ischemia and reperfusion.
-
- Antonino T., Riccardo D.S., Domenico D.R., Claudio P., Sergio L.P., Antonio P., Giuseppe L. Effects of clinical and laboratory variables and of pretreatment with cardiovascular drugs in acute ischaemic stroke: A retrospective chart review from the GIFA study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2011;151:318–322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

