Rad52 Restrains Resection at DNA Double-Strand Break Ends in Yeast
- PMID: 31542296
- PMCID: PMC6898758
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.08.017
Rad52 Restrains Resection at DNA Double-Strand Break Ends in Yeast
Abstract
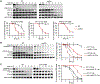
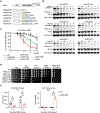
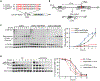
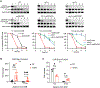
Rad52 is a key factor for homologous recombination (HR) in yeast. Rad52 helps assemble Rad51-ssDNA nucleoprotein filaments that catalyze DNA strand exchange, and it mediates single-strand DNA annealing. We find that Rad52 has an even earlier function in HR in restricting DNA double-stranded break ends resection that generates 3' single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) tails. In fission yeast, Exo1 is the primary resection nuclease, with the helicase Rqh1 playing a minor role. We demonstrate that the choice of two extensive resection pathways is regulated by Rad52. In rad52 cells, the resection rate increases from ∼3-5 kb/h up to ∼10-20 kb/h in an Rqh1-dependent manner, while Exo1 becomes dispensable. Budding yeast Rad52 similarly inhibits Sgs1-dependent resection. Single-molecule analysis with purified budding yeast proteins shows that Rad52 competes with Sgs1 for DNA end binding and inhibits Sgs1 translocation along DNA. These results identify a role for Rad52 in limiting ssDNA generated by end resection.
Keywords: DNA repair; Rad52; RecQ helicase; double-strand break; homologous recombination; resection; yeast.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A DNA nick at Ku-blocked double-strand break ends serves as an entry site for exonuclease 1 (Exo1) or Sgs1-Dna2 in long-range DNA end resection.J Biol Chem. 2018 Nov 2;293(44):17061-17069. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004769. Epub 2018 Sep 17. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30224356 Free PMC article.
-
The non-homologous end-joining factor Nej1 inhibits resection mediated by Dna2-Sgs1 nuclease-helicase at DNA double strand breaks.J Biol Chem. 2017 Sep 1;292(35):14576-14586. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.796011. Epub 2017 Jul 5. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28679532 Free PMC article.
-
Release of Ku and MRN from DNA ends by Mre11 nuclease activity and Ctp1 is required for homologous recombination repair of double-strand breaks.PLoS Genet. 2011 Sep;7(9):e1002271. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002271. Epub 2011 Sep 8. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21931565 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast as a model system to study RecQ helicase function.DNA Repair (Amst). 2010 Mar 2;9(3):303-14. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2009.12.007. Epub 2010 Jan 13. DNA Repair (Amst). 2010. PMID: 20071248 Review.
-
Maintenance of Yeast Genome Integrity by RecQ Family DNA Helicases.Genes (Basel). 2020 Feb 18;11(2):205. doi: 10.3390/genes11020205. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32085395 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms restraining break-induced replication at two-ended DNA double-strand breaks.EMBO J. 2021 May 17;40(10):e104847. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020104847. Epub 2021 Apr 12. EMBO J. 2021. PMID: 33844333 Free PMC article.
-
Single-molecule fluorescence imaging techniques reveal molecular mechanisms underlying deoxyribonucleic acid damage repair.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Sep 15;10:973314. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.973314. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36185427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative Lengthening of Telomeres: Building Bridges To Connect Chromosome Ends.Trends Cancer. 2020 Mar;6(3):247-260. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2019.12.009. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Trends Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32101727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Msc1 is a nuclear envelope protein that reinforces DNA repair in late mitosis.iScience. 2024 Jun 11;27(7):110250. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110250. eCollection 2024 Jul 19. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39021806 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering Bleomycin-Induced Genomic Alterations and Underlying Mechanisms in the Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Jan 25;88(2):e0170321. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01703-21. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 34731050 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

