B-cell-specific IRF4 deletion accelerates chronic lymphocytic leukemia development by enhanced tumor immune evasion
- PMID: 31537531
- PMCID: PMC6895374
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2019000973
B-cell-specific IRF4 deletion accelerates chronic lymphocytic leukemia development by enhanced tumor immune evasion
Abstract
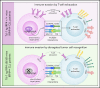
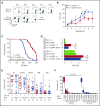
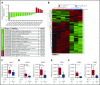
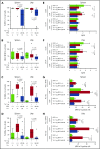
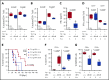
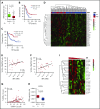
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a heterogenous disease that is highly dependent on a cross talk of CLL cells with the microenvironment, in particular with T cells. T cells derived from CLL patients or murine CLL models are skewed to an antigen-experienced T-cell subset, indicating a certain degree of antitumor recognition, but they are also exhausted, preventing an effective antitumor immune response. Here we describe a novel mechanism of CLL tumor immune evasion that is independent of T-cell exhaustion, using B-cell-specific deletion of the transcription factor IRF4 (interferon regulatory factor 4) in Tcl-1 transgenic mice developing a murine CLL highly similar to the human disease. We show enhanced CLL disease progression in IRF4-deficient Tcl-1 tg mice, associated with a severe downregulation of genes involved in T-cell activation, including genes involved in antigen processing/presentation and T-cell costimulation, which massively reduced T-cell subset skewing and exhaustion. We found a strong analogy in the human disease, with inferior prognosis of CLL patients with low IRF4 expression in independent CLL patient cohorts, failed T-cell skewing to antigen-experienced subsets, decreased costimulation capacity, and downregulation of genes involved in T-cell activation. These results have therapeutic relevance because our findings on molecular mechanisms of immune privilege may be responsible for the failure of immune-therapeutic strategies in CLL and may lead to improved targeting in the future.
© 2019 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Accelerated development of chronic lymphocytic leukemia in New Zealand Black mice expressing a low level of interferon regulatory factor 4.J Biol Chem. 2013 Sep 13;288(37):26430-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.475913. Epub 2013 Jul 29. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23897826 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon regulatory factor 4 attenuates Notch signaling to suppress the development of chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 5;7(27):41081-41094. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9596. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27232759 Free PMC article.
-
T Cells in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: A Two-Edged Sword.Front Immunol. 2021 Jan 20;11:612244. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.612244. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33552073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia induces an exhausted T cell phenotype in the TCL1 transgenic mouse model.Br J Haematol. 2015 Aug;170(4):515-22. doi: 10.1111/bjh.13467. Epub 2015 May 4. Br J Haematol. 2015. PMID: 25940792 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-talk between leukemic and immune cells at the tumor microenvironment in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: An update review.Eur J Haematol. 2024 Jul;113(1):4-15. doi: 10.1111/ejh.14224. Epub 2024 May 2. Eur J Haematol. 2024. PMID: 38698678 Review.
Cited by
-
IRF7 inhibits the Warburg effect via transcriptional suppression of PKM2 in osteosarcoma.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Jan 1;18(1):30-42. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.65255. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 34975316 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse Models in the Study of Mature B-Cell Malignancies.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2021 Apr 1;11(4):a034827. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a034827. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2021. PMID: 32398289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IRF4 modulates the response to BCR activation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia regulating IKAROS and SYK.Leukemia. 2021 May;35(5):1330-1343. doi: 10.1038/s41375-021-01178-5. Epub 2021 Feb 23. Leukemia. 2021. PMID: 33623139
-
The multiple roles of interferon regulatory factor family in health and disease.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Oct 9;9(1):282. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01980-4. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39384770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dynamic functions of IRF4 in B cell malignancies.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Aug;23(4):1171-1180. doi: 10.1007/s10238-022-00968-0. Epub 2022 Dec 10. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 36495369 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(1):7-34. - PubMed
-
- Sant M, Allemani C, Tereanu C, et al. ; HAEMACARE Working Group . Incidence of hematologic malignancies in Europe by morphologic subtype: results of the HAEMACARE project. Blood. 2010;116(19):3724-3734. - PubMed
-
- Kröber A, Seiler T, Benner A, et al. . V(H) mutation status, CD38 expression level, genomic aberrations, and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2002;100(4):1410-1416. - PubMed
-
- Zenz T, Mertens D, Küppers R, Döhner H, Stilgenbauer S. From pathogenesis to treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10(1):37-50. - PubMed
-
- Pleyer L, Egle A, Hartmann TN, Greil R. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of CLL: novel therapeutic approaches. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2009;6(7):405-418. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

