The immunomodulatory functions and molecular mechanism of a new bursal heptapeptide (BP7) in immune responses and immature B cells
- PMID: 31533803
- PMCID: PMC6749628
- DOI: 10.1186/s13567-019-0682-7
The immunomodulatory functions and molecular mechanism of a new bursal heptapeptide (BP7) in immune responses and immature B cells
Erratum in
-
Correction to: The immunomodulatory functions and molecular mechanism of a new bursal heptapeptide (BP7) in immune responses and immature B cells.Vet Res. 2021 Feb 16;52(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13567-020-00884-9. Vet Res. 2021. PMID: 33593407 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
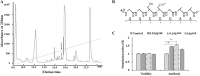
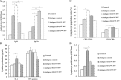
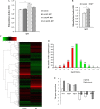
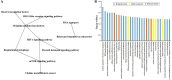
The bursa of Fabricius (BF) is the acknowledged central humoural immune organ unique to birds and plays a vital role in B lymphocyte development. In addition, the unique molecular immune features of bursal-derived biological peptides involved in B cell development are rarely reported. In this paper, a novel bursal heptapeptide (BP7) with the sequence GGCDGAA was isolated from the BF and was shown to enhance the monoclonal antibody production of a hybridoma. A mouse immunization experiment showed that mice immunized with an AIV antigen and BP7 produced strong antibody responses and cell-mediated immune responses. Additionally, BP7 stimulated increased mRNA levels of sIgM in immature mouse WEHI-231 B cells. Gene microarray results confirmed that BP7 regulated 2465 differentially expressed genes in BP7-treated WEHI-231 cells and induced 13 signalling pathways and various immune-related functional processes. Furthermore, we found that BP7 stimulated WEHI-231 cell autophagy and AMPK-ULK1 phosphorylation and regulated Bcl-2 protein expression. Finally, chicken immunization showed that BP7 enhanced the potential antibody and cytokine responses to the AIV antigen. These results suggested that BP7 might be an active biological factor that functions as a potential immunopotentiator, which provided some novel insights into the molecular mechanisms of the effects of bursal peptides on immune functions and B cell differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Functions and Mechanism of a New Oligopeptide BP9 from Avian Bursa on Antibody Responses, Immature B Cell, and Autophagy.J Immunol Res. 2019 Jan 6;2019:1574383. doi: 10.1155/2019/1574383. eCollection 2019. J Immunol Res. 2019. PMID: 30723747 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and immunomodulatory activity of bursal peptide, a novel bursal peptide from the chicken bursa of Fabricius.J Vet Sci. 2015;16(4):501-7. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2015.16.4.501. J Vet Sci. 2015. PMID: 26119163 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of Bursal Nonapeptide (BP9) on AIV Vaccine Immune Response in Chick Immunization and on Avian Immature B Cell.Protein Pept Lett. 2019;26(12):940-948. doi: 10.2174/0929866526666190730101455. Protein Pept Lett. 2019. PMID: 31362650
-
Antibodies, immunoglobulin genes and the bursa of Fabricius in chicken B cell development.Dev Comp Immunol. 2006;30(1-2):101-18. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2005.06.018. Dev Comp Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16139886 Review.
-
Somatic diversification of the chicken immunoglobulin light-chain gene.Adv Immunol. 1990;48:41-67. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60751-8. Adv Immunol. 1990. PMID: 2112303 Review.
Cited by
-
Clarification of a unique mucosal vaccination route for improved systemic and mucosal immune response in broiler.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 19;10(20):e39621. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39621. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39497952 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy and beyond: Unraveling the complexity of UNC-51-like kinase 1 (ULK1) from biological functions to therapeutic implications.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Oct;12(10):3743-3782. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.06.004. Epub 2022 Jun 11. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 36213540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The molecular evolutionary characteristics of new isolated H9N2 AIV from East China and the function of vimentin on virus replication in MDCK cells.Virol J. 2020 Jun 17;17(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s12985-020-01351-9. Virol J. 2020. PMID: 32552884 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analysis of spleen B cell revealed the molecular basis of bursopentin on B cell differentiation.Vet Res. 2022 Dec 14;53(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s13567-022-01123-z. Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 36517897 Free PMC article.
-
Correction to: The immunomodulatory functions and molecular mechanism of a new bursal heptapeptide (BP7) in immune responses and immature B cells.Vet Res. 2021 Feb 16;52(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13567-020-00884-9. Vet Res. 2021. PMID: 33593407 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ratcliffe MJH, Härtle S. B cells, the bursa of Fabricius and the generation of antibody repertoires. In: Schat KA, Kaspars B, Kaiser P, editors. Avian immunology. Hoboken: Elsevier; 2014. pp. 65–89.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

