First Days in the Life of Naive Human B Lymphocytes Infected with Epstein-Barr Virus
- PMID: 31530670
- PMCID: PMC6751056
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.01723-19
First Days in the Life of Naive Human B Lymphocytes Infected with Epstein-Barr Virus
Abstract
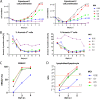
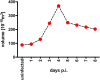
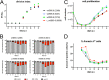
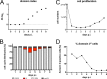
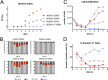
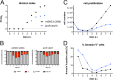
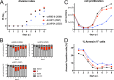
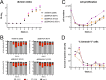
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infects and activates resting human B lymphocytes, reprograms them, induces their proliferation, and establishes a latent infection in them. In established EBV-infected cell lines, many viral latent genes are expressed. Their roles in supporting the continuous proliferation of EBV-infected B cells in vitro are known, but their functions in the early, prelatent phase of infection have not been investigated systematically. In studies during the first 8 days of infection using derivatives of EBV with mutations in single genes of EBVs, we found only Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA2) to be essential for activating naive human B lymphocytes, inducing their growth in cell volume, driving them into rapid cell divisions, and preventing cell death in a subset of infected cells. EBNA-LP, latent membrane protein 2A (LMP2A), and the viral microRNAs have supportive, auxiliary functions, but mutants of LMP1, EBNA3A, EBNA3C, and the noncoding Epstein-Barr virus with small RNA (EBERs) had no discernible phenotype compared with wild-type EBV. B cells infected with a double mutant of EBNA3A and 3C had an unexpected proliferative advantage and did not regulate the DNA damage response (DDR) of the infected host cell in the prelatent phase. Even EBNA1, which has very critical long-term functions in maintaining and replicating the viral genomic DNA in established cell lines, was dispensable for the early activation of infected cells. Our findings document that the virus dose is a decisive parameter and indicate that EBNA2 governs the infected cells initially and implements a strictly controlled temporal program independent of other viral latent genes. It thus appears that EBNA2 is sufficient to control all requirements for clonal cellular expansion and to reprogram human B lymphocytes from energetically quiescent to activated cells.IMPORTANCE The preferred target of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is human resting B lymphocytes. We found that their infection induces a well-coordinated, time-driven program that starts with a substantial increase in cell volume, followed by cellular DNA synthesis after 3 days and subsequent rapid rounds of cell divisions on the next day accompanied by some DNA replication stress (DRS). Two to 3 days later, the cells decelerate and turn into stably proliferating lymphoblast cell lines. With the aid of 16 different recombinant EBV strains, we investigated the individual contributions of EBV's multiple latent genes during early B-cell infection and found that many do not exert a detectable phenotype or contribute little to EBV's prelatent phase. The exception is EBNA2 that is essential in governing all aspects of B-cell reprogramming. EBV relies on EBNA2 to turn the infected B lymphocytes into proliferating lymphoblasts preparing the infected host cell for the ensuing stable, latent phase of viral infection. In the early steps of B-cell reprogramming, viral latent genes other than EBNA2 are dispensable, but some, EBNA-LP, for example, support the viral program and presumably stabilize the infected cells once viral latency is established.
Keywords: B lymphocytes; human herpesviruses; reprogramming; transformation.
Copyright © 2019 Pich et al.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen EBNA-LP is essential for transforming naïve B cells, and facilitates recruitment of transcription factors to the viral genome.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Feb 20;14(2):e1006890. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006890. eCollection 2018 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29462212 Free PMC article.
-
EBNA2-deleted Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) isolate, P3HR1, causes Hodgkin-like lymphomas and diffuse large B cell lymphomas with type II and Wp-restricted latency types in humanized mice.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Jun 15;16(6):e1008590. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008590. eCollection 2020 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32542010 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Nuclear Antigen 3 (EBNA3) Proteins Regulate EBNA2 Binding to Distinct RBPJ Genomic Sites.J Virol. 2015 Dec 30;90(6):2906-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02737-15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26719268 Free PMC article.
-
EBNA2 and Its Coactivator EBNA-LP.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;391:35-59. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22834-1_2. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26428371 Review.
-
Human B cells on their route to latent infection--early but transient expression of lytic genes of Epstein-Barr virus.Eur J Cell Biol. 2012 Jan;91(1):65-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2011.01.014. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Eur J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 21450364 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Dendritic Cells in Immune Control and Vaccination against -Herpesviruses.Viruses. 2019 Dec 5;11(12):1125. doi: 10.3390/v11121125. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31817510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LMP1 and EBNA2 constitute a minimal set of EBV genes for transformation of human B cells.Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 19;14:1331730. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1331730. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38169736 Free PMC article.
-
Replication Compartments-The Great Survival Strategy for Epstein-Barr Virus Lytic Replication.Microorganisms. 2022 Apr 25;10(5):896. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10050896. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35630341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple Viral microRNAs Regulate Interferon Release and Signaling Early during Infection with Epstein-Barr Virus.mBio. 2021 Mar 30;12(2):e03440-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03440-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33785626 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein-driven B cell metabolism remodeling.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Feb 2;18(2):e1010254. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010254. eCollection 2022 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35108325 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
