Ribosomal Protein L15 is involved in Colon Carcinogenesis
- PMID: 31523176
- PMCID: PMC6743284
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.34386
Ribosomal Protein L15 is involved in Colon Carcinogenesis
Abstract
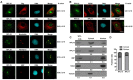
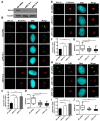
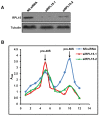
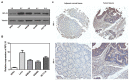
Ribosomal biogenesis is responsible for protein synthesis in all eukaryotic cells. Perturbation of ribosomal biogenesis processes can cause dysfunctions of protein synthesis and varieties of human diseases. In this study, we examine the role of RPL15, a large ribosomal subunit protein, in human colon carcinogenesis. Our results reveal that RPL15 is remarkably upregulated in human primary colon cancer tissues and cultured cell lines when compared with paired non-cancerous tissues and non-transformed epithelium cells. Elevated expression of RPL15 in colon cancer tissues is closely correlated with clinicopathological characteristics in patients. We determine the effects of RPL15 on nucleolar maintenance, ribosomal biogenesis and cell proliferation in human cells. We show that RPL15 is required for maintenance of nucleolar structure and formation of pre-60S subunits in the nucleoli. Depletion of RPL15 causes ribosomal stress, resulting in a G1-G1/S cell cycle arrest in non-transformed human epithelium cells, but apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Together, these results indicate that RPL15 is involved in human colon carcinogenesis and might be a potential clinical biomarker and/or target for colon cancer therapy.
Keywords: RPL RPL15; apoptosis; apoptosis 15; colon cancer; nucleolus; ribosome biogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The roles of RRP15 in nucleolar formation, ribosome biogenesis and checkpoint control in human cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 21;8(8):13240-13252. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14658. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28099941 Free PMC article.
-
Role of uL3 in the Crosstalk between Nucleolar Stress and Autophagy in Colon Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 20;21(6):2143. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062143. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32244996 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of RPL15 may predict poor survival and associate with tumor progression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 10;6(35):37028-42. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5939. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26498693 Free PMC article.
-
Principles of 60S ribosomal subunit assembly emerging from recent studies in yeast.Biochem J. 2017 Jan 15;474(2):195-214. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160516. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 28062837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ribosomal Proteins Control or Bypass p53 during Nucleolar Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jan 12;18(1):140. doi: 10.3390/ijms18010140. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28085118 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RPL15 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via regulation of RPs-MDM2-p53 signaling pathway.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Apr 11;22(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02555-5. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 35410346 Free PMC article.
-
RPL24 as a potential prognostic biomarker for cervical cancer treated by Cisplatin and concurrent chemoradiotherapy.Front Oncol. 2023 Oct 18;13:1131803. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1131803. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37920171 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal proteins and human diseases: molecular mechanisms and targeted therapy.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Aug 30;6(1):323. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00728-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34462428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The predictive value of RNA binding proteins in colon adenocarcinoma.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021 Aug;12(4):1543-1557. doi: 10.21037/jgo-21-318. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34532109 Free PMC article.
-
RPL34-AS1-induced RPL34 inhibits cervical cancer cell tumorigenesis via the MDM2-P53 pathway.Cancer Sci. 2021 May;112(5):1811-1821. doi: 10.1111/cas.14874. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 33675124 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

