FunDMDeep-m6A: identification and prioritization of functional differential m6A methylation genes
- PMID: 31510685
- PMCID: PMC6612877
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz316
FunDMDeep-m6A: identification and prioritization of functional differential m6A methylation genes
Abstract
Motivation: As the most abundant mammalian mRNA methylation, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) exists in >25% of human mRNAs and is involved in regulating many different aspects of mRNA metabolism, stem cell differentiation and diseases like cancer. However, our current knowledge about dynamic changes of m6A levels and how the change of m6A levels for a specific gene can play a role in certain biological processes like stem cell differentiation and diseases like cancer is largely elusive.
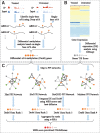
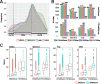
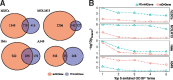
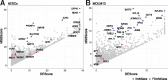
Results: To address this, we propose in this paper FunDMDeep-m6A a novel pipeline for identifying context-specific (e.g. disease versus normal, differentiated cells versus stem cells or gene knockdown cells versus wild-type cells) m6A-mediated functional genes. FunDMDeep-m6A includes, at the first step, DMDeep-m6A a novel method based on a deep learning model and a statistical test for identifying differential m6A methylation (DmM) sites from MeRIP-Seq data at a single-base resolution. FunDMDeep-m6A then identifies and prioritizes functional DmM genes (FDmMGenes) by combing the DmM genes (DmMGenes) with differential expression analysis using a network-based method. This proposed network method includes a novel m6A-signaling bridge (MSB) score to quantify the functional significance of DmMGenes by assessing functional interaction of DmMGenes with their signaling pathways using a heat diffusion process in protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks. The test results on 4 context-specific MeRIP-Seq datasets showed that FunDMDeep-m6A can identify more context-specific and functionally significant FDmMGenes than m6A-Driver. The functional enrichment analysis of these genes revealed that m6A targets key genes of many important context-related biological processes including embryonic development, stem cell differentiation, transcription, translation, cell death, cell proliferation and cancer-related pathways. These results demonstrate the power of FunDMDeep-m6A for elucidating m6A regulatory functions and its roles in biological processes and diseases.
Availability and implementation: The R-package for DMDeep-m6A is freely available from https://github.com/NWPU-903PR/DMDeepm6A1.0.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Global analysis of N6-methyladenosine functions and its disease association using deep learning and network-based methods.PLoS Comput Biol. 2019 Jan 2;15(1):e1006663. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006663. eCollection 2019 Jan. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019. PMID: 30601803 Free PMC article.
-
Funm6AViewer: a web server and R package for functional analysis of context-specific m6A RNA methylation.Bioinformatics. 2021 Nov 18;37(22):4277-4279. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btab362. Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 33974000
-
N6-methyladenosine methylation analysis of long noncoding RNAs and mRNAs in 5-FU-resistant colon cancer cells.Epigenetics. 2024 Dec;19(1):2298058. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2023.2298058. Epub 2023 Dec 25. Epigenetics. 2024. PMID: 38145548 Free PMC article.
-
RNA m6A modifications in mammalian gametogenesis and pregnancy.Reproduction. 2022 Dec 2;165(1):R1-R8. doi: 10.1530/REP-22-0112. Print 2023 Jan 1. Reproduction. 2022. PMID: 36194446 Review.
-
Functions of N6-methyladenosine and its role in cancer.Mol Cancer. 2019 Dec 4;18(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1109-9. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31801551 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential and Common Signatures of miRNA Expression and Methylation in Childhood Central Nervous System Malignancies: An Experimental and Computational Approach.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 31;13(21):5491. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215491. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771655 Free PMC article.
-
Expression pattern and prognostic value of N6-methyladenosine RNA methylation key regulators in hepatocellular carcinoma.Mutagenesis. 2021 Oct 6;36(5):369-379. doi: 10.1093/mutage/geab032. Mutagenesis. 2021. PMID: 34467992 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the functional roles of N6-methyladenosine modification in cancer progression: mechanisms and clinical implications.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jun;49(6):4929-4941. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07126-5. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35025029 Review.
-
m6A-express: uncovering complex and condition-specific m6A regulation of gene expression.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Nov 18;49(20):e116. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab714. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34417605 Free PMC article.
-
Computational identification of eukaryotic promoters based on cascaded deep capsule neural networks.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Jul 20;22(4):bbaa299. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaa299. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33227813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benjamini Y., Hochberg Y. (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate – a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. B, 57, 289–300.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

