Current Insights into the Role of the Growth Hormone-Insulin-Like Growth Factor System in Short Children Born Small for Gestational Age
- PMID: 31509834
- PMCID: PMC6979433
- DOI: 10.1159/000502739
Current Insights into the Role of the Growth Hormone-Insulin-Like Growth Factor System in Short Children Born Small for Gestational Age
Abstract
Background: The reason for the insufficient catch-up growth seen in 10% of children born small for gestational age (SGA) is poorly understood. Disturbances in the growth hormone (GH) - insulin-like growth factor (IGF) axis might underlie this failure to show sufficient catch-up growth.
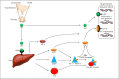
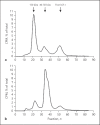
Conclusion: This review summarizes insights gained in the molecular and (epi) genetic mechanisms of the GH-IGF axis in short children born SGA. The most notable anomalies of the IGF system are the lowered IGF-I levels in both cord blood and the placenta, and the increased expression of IGF-binding proteins (IGFBP)-1 and IGFBP-2, which inhibit IGF-I, in the placenta of SGA neonates. These observations suggest a decreased bioactivity of IGF-I in utero. IGF-I levels remain reduced in SGA children with short stature, as well as IGFBP-3 and acid-labile subunit levels. Proteolysis of IGFBP-3 appears to be increased.
Keywords: Acid-labile subunit; Growth hormone; Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins; Small for gestational age; Ternary complex formation.
© 2019 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
A.C.S.H.-K. received an independent research grant from Novo Nordisk BV (The Netherlands) for the investigator-initiated studies. The remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic and epigenetic variability in the gene for IGFBP-3 (IGFBP3): correlation with serum IGFBP-3 levels and growth in short children born small for gestational age.Growth Horm IGF Res. 2009 Jun;19(3):198-205. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2008.08.010. Epub 2008 Oct 16. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2009. PMID: 18929499 Clinical Trial.
-
Sensitivity to IGF-I in short children born small for gestational age.J Endocrinol Invest. 2006;29(1 Suppl):21-6. J Endocrinol Invest. 2006. PMID: 16615303 Review.
-
IGF-I and IGF binding protein-3 levels during initial GH dosage step-up are indicators of GH sensitivity in GH-deficient children and short children born small for gestational age.Horm Res. 2005;64(2):68-76. doi: 10.1159/000087692. Epub 2005 Aug 19. Horm Res. 2005. PMID: 16113581
-
Changes in serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding protein-3 levels during growth hormone treatment in prepubertal short children born small for gestational age.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996 Nov;81(11):3902-8. doi: 10.1210/jcem.81.11.8923836. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996. PMID: 8923836
-
Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins in children born small for gestational age: implication for growth hormone therapy.Horm Res. 2003;60 Suppl 3:115-23. doi: 10.1159/000074512. Horm Res. 2003. PMID: 14671408 Review.
Cited by
-
Growth hormone treatment does not to lead to insulin resistance nor excessive rise in IGF-1 levels, while improving height in patients small for gestational age A long-term observational study.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2022 Apr;96(4):558-568. doi: 10.1111/cen.14626. Epub 2021 Dec 9. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2022. PMID: 34882803 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive peptides identification and nutritional status ameliorating properties on malnourished rats of combined eel and soy-based tempe flour.Front Nutr. 2022 Sep 28;9:963065. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.963065. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36245543 Free PMC article.
-
The Variability of Growth and Puberty in Growth Hormone-treated Children Born Small for Gestational Age.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Sep 28;107(10):e4263-e4264. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac357. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 35731578 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Vitamin D status and VDR gene polymorphisms in patients with growth hormone deficiency: A case control Tunisian study.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 20;10(14):e34947. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34947. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39149044 Free PMC article.
-
Adult-Onset Diseases in Low Birth Weight Infants: Association with Adipose Tissue Maldevelopment.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2020 May 1;27(5):397-405. doi: 10.5551/jat.RV17039. Epub 2019 Dec 20. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2020. PMID: 31866623 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Karlberg J, Albertsson-Wikland K. Growth in full-term small-for-gestational-age infants: from birth to final height. Pediatr Res. 1995 Nov;38((5)):733–9. - PubMed
-
- Clayton PE, Cianfarani S, Czernichow P, Johannsson G, Rapaport R, Rogol A. Management of the child born small for gestational age through to adulthood: a consensus statement of the International Societies of Pediatric Endocrinology and the Growth Hormone Research Society. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007 Mar;92((3)):804–10. - PubMed
-
- Bryan SM, Hindmarsh PC. Normal and abnormal fetal growth. Horm Res. 2006;65(Suppl 3):19–27. - PubMed
-
- Finken MJ, van der Steen M, Smeets CC, Walenkamp MJ, de Bruin C, Hokken-Koelega AC, et al. Children Born Small for Gestational Age: Differential Diagnosis, Molecular Genetic Evaluation, and Implications. Endocr Rev. 2018 Dec;39((6)):851–94. - PubMed
-
- Hokken-Koelega AC, De Ridder MA, Lemmen RJ, Den Hartog H, De Muinck Keizer-Schrama SM, Drop SL. Children born small for gestational age: do they catch up? Pediatr Res. 1995 Aug;38((2)):267–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

