Immunomodulatory Nanosystems
- PMID: 31508270
- PMCID: PMC6724480
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.201900101
Immunomodulatory Nanosystems
Abstract
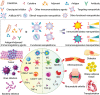
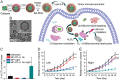
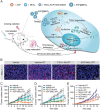
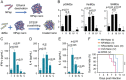
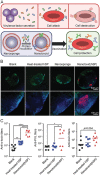
Immunotherapy has emerged as an effective strategy for the prevention and treatment of a variety of diseases, including cancer, infectious diseases, inflammatory diseases, and autoimmune diseases. Immunomodulatory nanosystems can readily improve the therapeutic effects and simultaneously overcome many obstacles facing the treatment method, such as inadequate immune stimulation, off-target side effects, and bioactivity loss of immune agents during circulation. In recent years, researchers have continuously developed nanomaterials with new structures, properties, and functions. This Review provides the most recent advances of nanotechnology for immunostimulation and immunosuppression. In cancer immunotherapy, nanosystems play an essential role in immune cell activation and tumor microenvironment modulation, as well as combination with other antitumor approaches. In infectious diseases, many encouraging outcomes from using nanomaterial vaccines against viral and bacterial infections have been reported. In addition, nanoparticles also potentiate the effects of immunosuppressive immune cells for the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Finally, the challenges and prospects of applying nanotechnology to modulate immunotherapy are discussed.
Keywords: disease treatment; immunostimulation; immunosuppression; immunotherapy; nanotechnology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Immunomodulatory nanosystems: An emerging strategy to combat viral infections.Biomater Biosyst. 2023 Jan 30;9:100073. doi: 10.1016/j.bbiosy.2023.100073. eCollection 2023 Mar. Biomater Biosyst. 2023. PMID: 36967725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticles as Smart Carriers for Enhanced Cancer Immunotherapy.Front Chem. 2020 Dec 21;8:597806. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2020.597806. eCollection 2020. Front Chem. 2020. PMID: 33409265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomaterials Enhance the Immunomodulatory Effect of Molecular Targeted Therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Mar 1;16:1631-1661. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S290346. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33688183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering vaccines and niches for immune modulation.Acta Biomater. 2014 Apr;10(4):1728-40. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2013.12.036. Epub 2013 Dec 27. Acta Biomater. 2014. PMID: 24373907 Review.
-
Hypoxia-modulatory nanomaterials to relieve tumor hypoxic microenvironment and enhance immunotherapy: Where do we stand?Acta Biomater. 2021 Apr 15;125:1-28. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.02.030. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Acta Biomater. 2021. PMID: 33639310 Review.
Cited by
-
Injectable Gelatin Hydrogel Suppresses Inflammation and Enhances Functional Recovery in a Mouse Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Jul 14;8:785. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00785. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32760708 Free PMC article.
-
Evolving understanding of autoimmune mechanisms and new therapeutic strategies of autoimmune disorders.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Oct 4;9(1):263. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01952-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39362875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymeric Micelles in Cancer Immunotherapy.Molecules. 2021 Feb 25;26(5):1220. doi: 10.3390/molecules26051220. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33668746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in pH-Responsive nanoparticles for osteoarthritis treatment: Opportunities and challenges.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jul 1;12:1426794. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1426794. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39036562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Situ-Activated Phospholipid-Mimic Artemisinin Prodrug via Injectable Hydrogel Nano/Microsphere for Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy.Research (Wash D C). 2022 Dec 15;2022:0003. doi: 10.34133/research.0003. eCollection 2022. Research (Wash D C). 2022. PMID: 39290968 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
