Role of the active zone protein, ELKS, in insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells
- PMID: 31500835
- PMCID: PMC6768504
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.06.017
Role of the active zone protein, ELKS, in insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells
Abstract
Background: Insulin is stored within large dense-core granules in pancreatic beta (β)-cells and is released by Ca2+-triggered exocytosis with increasing blood glucose levels. Polarized and targeted secretion of insulin from β-cells in pancreatic islets into the vasculature has been proposed; however, the mechanisms related to cellular and molecular localization remain largely unknown. Within nerve terminals, the Ca2+-dependent release of a polarized transmitter is limited to the active zone, a highly specialized area of the presynaptic membrane. Several active zone-specific proteins have been characterized; among them, the CAST/ELKS protein family members have the ability to form large protein complexes with other active zone proteins to control the structure and function of the active zone for tight regulation of neurotransmitter release. Notably, ELKS but not CAST is also expressed in β-cells, implying that ELKS may be involved in polarized insulin secretion from β-cells.
Scope of review: This review provides an overview of the current findings regarding the role(s) of ELKS and other active zone proteins in β-cells and focuses on the molecular mechanism underlying ELKS regulation within polarized insulin secretion from islets.
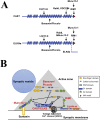
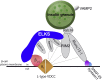
Major conclusions: ELKS localizes at the vascular-facing plasma membrane of β-cells in mouse pancreatic islets. ELKS forms a potent insulin secretion complex with L-type voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels on the vascular-facing plasma membrane of β-cells, enabling polarized Ca2+ influx and first-phase insulin secretion from islets. This model provides novel insights into the functional polarity observed during insulin secretion from β-cells within islets at the molecular level. This active zone-like region formed by ELKS at the vascular side of the plasma membrane is essential for coordinating physiological insulin secretion and may be disrupted in diabetes.
Keywords: Active zone protein; Ca(2+) influx; ELKS; Insulin exocytosis; Pancreatic β-cells; Voltage-dependent Ca(2+) channel.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier GmbH.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ELKS/Voltage-Dependent Ca2+ Channel-β Subunit Module Regulates Polarized Ca2+ Influx in Pancreatic β Cells.Cell Rep. 2019 Jan 29;26(5):1213-1226.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.12.106. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 30699350
-
ELKS, a protein structurally related to the active zone-associated protein CAST, is expressed in pancreatic beta cells and functions in insulin exocytosis: interaction of ELKS with exocytotic machinery analyzed by total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Jul;16(7):3289-300. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-09-0816. Epub 2005 May 11. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15888548 Free PMC article.
-
ELKS active zone proteins as multitasking scaffolds for secretion.Open Biol. 2018 Feb;8(2):170258. doi: 10.1098/rsob.170258. Open Biol. 2018. PMID: 29491150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ELKS, a protein structurally related to the active zone protein CAST, is involved in Ca2+-dependent exocytosis from PC12 cells.Genes Cells. 2006 Jun;11(6):659-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2006.00970.x. Genes Cells. 2006. PMID: 16716196
-
Presynaptic-like mechanisms and the control of insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cells.Cell Calcium. 2022 Jun;104:102585. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2022.102585. Epub 2022 Mar 28. Cell Calcium. 2022. PMID: 35405569 Review.
Cited by
-
Directed insulin secretion occurs at precise cortical regions with optimal ELKS content that are devoid of microtubules.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 1:2024.10.31.621333. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.31.621333. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39553950 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Angiopoietins stimulate pancreatic islet development from stem cells.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 30;11(1):13558. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-92922-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34193893 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin granule biogenesis and exocytosis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Mar;78(5):1957-1970. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03688-4. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33146746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microtubules in Pancreatic β Cells: Convoluted Roadways Toward Precision.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jul 8;10:915206. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.915206. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35874834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microtubules regulate pancreatic β-cell heterogeneity via spatiotemporal control of insulin secretion hot spots.Elife. 2021 Nov 16;10:e59912. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59912. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34783306 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonner-Weir S. Morphological evidence for pancreatic polarity of β-cell within islets of langerhans. Diabetes. 1988;37(5):616–621. - PubMed
-
- Roscioni S.S., Migliorini A., Gegg M., Lickert H. Impact of islet architecture on β-cell heterogeneity, plasticity and function. Nature Reviews Endocrinology. 2016;12(12):695–709. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

