Maternal Creatine Supplementation Positively Affects Male Rat Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity in Adult Offspring
- PMID: 31461895
- PMCID: PMC6770830
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11092014
Maternal Creatine Supplementation Positively Affects Male Rat Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity in Adult Offspring
Abstract
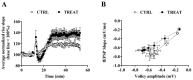
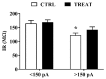
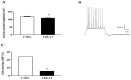
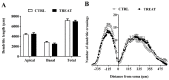
Creatine plays a crucial role in developing the brain, so much that its genetic deficiency results in mental dysfunction and cognitive impairments. Moreover, creatine supplementation is currently under investigation as a preventive measure to protect the fetus against oxidative stress during difficult pregnancies. Although creatine use is considered safe, posing minimal risk to clinical health, we found an alteration in morpho-functional maturation of neurons when male rats were exposed to creatine loads during brain development. In particular, increased excitability and enhanced long-term potentiation (LTP) were observed in the hippocampal pyramidal neurons of weaning pups. Since these effects were observed a long time after creatine treatment had been terminated, long-lasting modifications persisting into adulthood were hypothesized. Such modifications were investigated in the present study using morphological, electrophysiological, and calcium imaging techniques applied to hippocampal Cornu Ammonis 1 (CA1) neurons of adult rats born from dams supplemented with creatine. When compared to age-matched controls, the treated adult offspring were found to retain enhanced neuron excitability and an improved LTP, the best-documented neuronal substrate for memory formation. While translating data from rats to humans does have limitations, our findings suggest that prenatal creatine supplementation could have positive effects on adult cognitive abilities.
Keywords: adult offspring; creatine supplementation; hippocampus; long-term potentiation; neuron excitability; prenatal treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
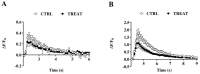
Similar articles
-
Maternal creatine supplementation affects the morpho-functional development of hippocampal neurons in rat offspring.Neuroscience. 2016 Jan 15;312:120-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.11.017. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Neuroscience. 2016. PMID: 26592720
-
Maternal dietary loads of α-tocopherol depress protein kinase C signaling and synaptic plasticity in rat postnatal developing hippocampus and promote permanent deficits in adult offspring.J Nutr Biochem. 2011 Jan;22(1):60-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2009.11.014. Epub 2010 Apr 10. J Nutr Biochem. 2011. PMID: 20382010
-
Prenatal administration of morphine decreases CREBSerine-133 phosphorylation and synaptic plasticity range mediated by glutamatergic transmission in the hippocampal CA1 area of cognitive-deficient rat offspring.Hippocampus. 2003;13(8):915-21. doi: 10.1002/hipo.10137. Hippocampus. 2003. PMID: 14750654
-
Maternal DHA supplementation protects rat offspring against impairment of learning and memory following prenatal exposure to valproic acid.J Nutr Biochem. 2016 Sep;35:87-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2016.07.003. Epub 2016 Jul 9. J Nutr Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27469996
-
Comparison Impairments of Spatial Cognition and Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity Between Prenatal and Postnatal Melamine Exposure in Male Adult Rats.Neurotox Res. 2016 Feb;29(2):218-29. doi: 10.1007/s12640-015-9578-0. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Neurotox Res. 2016. PMID: 26607910
Cited by
-
GABAergic Input Affects Intracellular Calcium Levels in Developing Granule Cells of Adult Rat Hippocampus.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 3;21(5):1715. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051715. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32138257 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of Adverse Outcomes in Females Taking Oral Creatine Monohydrate: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Nutrients. 2020 Jun 15;12(6):1780. doi: 10.3390/nu12061780. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32549301 Free PMC article.
-
5HT1AR-FGFR1 Heteroreceptor Complexes Differently Modulate GIRK Currents in the Dorsal Hippocampus and the Dorsal Raphe Serotonin Nucleus of Control Rats and of a Genetic Rat Model of Depression.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 18;24(8):7467. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087467. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108630 Free PMC article.
-
Calsequestrin Deletion Facilitates Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity and Spatial Learning in Post-Natal Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 31;21(15):5473. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155473. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32751833 Free PMC article.
-
Nutraceuticals in the Prevention of Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia: A Comprehensive Review of their Neuroprotective Properties, Mechanisms of Action and Future Directions.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 3;22(5):2524. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052524. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33802413 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chung Y.L., Alexanderson H., Pipitone N., Morrison C., Dastmalchi M., Stahl-Hallengren C., Richards S., Thomas E.L., Hamilton G., Bell J.D., et al. Creatine supplements in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies who are clinically weak after conventional pharmacologic treatment: Six-month, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;57:694–702. doi: 10.1002/art.22687. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schulze A., Battini R. Pre-symptomatic treatment of creatine biosynthesis defects. Sub-Cell. Biochem. 2007;46:167–181. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

