Anti-hypertensive Effect of Cereal Antioxidant Ferulic Acid and Its Mechanism of Action
- PMID: 31448280
- PMCID: PMC6692439
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2019.00121
Anti-hypertensive Effect of Cereal Antioxidant Ferulic Acid and Its Mechanism of Action
Abstract
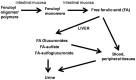
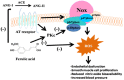
Ferulic acid is a simple phenolic acid found mainly in cereals and grains, used as an antioxidant and food preservative. Recent evidence suggests that ferulic acid possess anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic, anticancer, and cardioprotective properties. Several investigations also have shown that ferulic acid rich food might prevent hypertension. As a potent scavenger of free radicals (ROS, reactive oxygen species), ferulic acid attenuates oxidative stress, which is responsible for lowering elevated blood-pressure through improved endothelial function and increased bioavailability of the nitric oxide in the arterial vasculature. This review article describes the role of ferulic acid in the pathophysiology of vascular dysfunction and hypertension along with highlighted the merit of further scientific and clinical exploration.
Keywords: NADPH oxidase; endothelium; ferulic acid; hypertension; reactive oxygen species.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Curcumin improves endothelial dysfunction and vascular remodeling in 2K-1C hypertensive rats by raising nitric oxide availability and reducing oxidative stress.Nitric Oxide. 2014 Nov 15;42:44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2014.09.001. Epub 2014 Sep 4. Nitric Oxide. 2014. PMID: 25194767
-
Reactive oxygen species, vascular oxidative stress, and redox signaling in hypertension: what is the clinical significance?Hypertension. 2004 Sep;44(3):248-52. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000138070.47616.9d. Epub 2004 Jul 19. Hypertension. 2004. PMID: 15262903 Review.
-
Doxycycline ameliorates 2K-1C hypertension-induced vascular dysfunction in rats by attenuating oxidative stress and improving nitric oxide bioavailability.Nitric Oxide. 2012 Mar 31;26(3):162-8. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2012.01.009. Epub 2012 Feb 3. Nitric Oxide. 2012. PMID: 22327038
-
Chlorogenic acid attenuates hypertension and improves endothelial function in spontaneously hypertensive rats.J Hypertens. 2006 Jun;24(6):1065-73. doi: 10.1097/01.hjh.0000226196.67052.c0. J Hypertens. 2006. PMID: 16685206
-
Interaction between nitric oxide and angiotensin II in the endothelium: role in atherosclerosis and hypertension.J Hypertens Suppl. 2006 Mar;24(1):S45-50. doi: 10.1097/01.hjh.0000220406.46246.f2. J Hypertens Suppl. 2006. PMID: 16601573 Review.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Digestibility and Bioaccessibility of Nutrients and Non-Nutrients Composing Extruded Brewers' Spent Grain.Nutrients. 2022 Aug 24;14(17):3480. doi: 10.3390/nu14173480. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36079739 Free PMC article.
-
Cycloartenyl Ferulate Is the Predominant Compound in Brown Rice Conferring Cytoprotective Potential against Oxidative Stress-Induced Cytotoxicity.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 3;24(1):822. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010822. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36614263 Free PMC article.
-
Plant Polyphenols and Their Potential Benefits on Cardiovascular Health: A Review.Molecules. 2023 Sep 1;28(17):6403. doi: 10.3390/molecules28176403. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37687232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Nanomaterials with Intrinsic Antioxidant Activity by Surface Functionalization of Niosomes with Natural Phenolic Acids.Pharmaceutics. 2021 May 21;13(6):766. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13060766. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34063874 Free PMC article.
-
Ferulic Acid Treats Gastric Ulcer via Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation.Life (Basel). 2023 Jan 31;13(2):388. doi: 10.3390/life13020388. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836745 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials