Differential expression of mGluRs in rat spinal dorsal horns and their modulatory effects on nocifensive behaviors
- PMID: 31432760
- PMCID: PMC6751533
- DOI: 10.1177/1744806919875026
Differential expression of mGluRs in rat spinal dorsal horns and their modulatory effects on nocifensive behaviors
Abstract
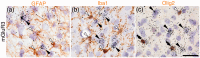
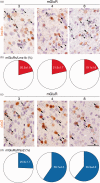
Glutamate is a neurotransmitter present in most excitatory synapses in the nervous system. It also plays a key role in the spinal cord’s physiological excitatory circuit and is involved in pathological neurotransmissions such as those observed in inflammatory and neuropathic pain conditions. The actions of glutamate are mediated by different types of ionotropic glutamate receptors (iGluRs) and metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs). Although expressions of iGluRs are well studied, those of mGluRs are not fully elucidated in the spinal cord. In this study, we examined the expressions of mGluRs (mGluR1-8) and investigated which mGluR subtypes can modulate pain transmission in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord using an inflammatory pain model. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction revealed that mGluR mRNAs, except for mGluR2 and 6, were detected in the spinal cord. Double labeling analysis, in situ hybridization histochemistry with immunohistochemistry, was used to examine the distribution of each mGluR in neurons or glial cells in the lamina I–II of the spinal dorsal horn. mGluR1, 5, and 7 were generally, and 4 and 8 were frequently, expressed in neurons. mGluR3 was expressed not only in neurons but also in oligodendrocytes. We next examined the distribution of mGluR4 and 8 were expressed in excitatory or inhibitory neurons. Both mGluR4 and 8 were preferentially expressed in inhibitory neurons rather than in excitatory neurons. Furthermore, intrathecal delivery of CPPG((RS)-α-cyclopropyl-4-phosphonophenylglycine), an antagonist for mGluR 4 and 8, attenuated nocifensive behaviors and the increase in fos-positive-excitatory neurons of the dorsal horn induced by intraplantar injection of formalin. These findings suggest that mGluR4 and 8, which are preferentially expressed in inhibitory neurons, may play roles in the modulation of pain transmission in the spinal dorsal horn.
Keywords: Glutamate; dorsal horn; formalin; metabotropic glutamate receptor; nociception; spinal cord.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of adenosine A 2A receptors in the rat lumbar spinal cord and implications in the modulation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor currents.Anesth Analg. 2008 Jun;106(6):1882-9. doi: 10.1213/ane.0b013e318173251f. Anesth Analg. 2008. PMID: 18499627
-
Isoflurane decreases substantia gelatinosa neuron excitability and synaptic transmission from periphery in the rat spinal dorsal horn.Neuroreport. 2021 Jan 13;32(2):77-81. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000001557. Neuroreport. 2021. PMID: 33323835
-
Glutamate and metabotropic glutamate receptors associated with innervation of the uterine cervix during pregnancy: receptor antagonism inhibits c-Fos expression in rat lumbosacral spinal cord at parturition.J Neurosci Res. 2007 May 1;85(6):1318-35. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21225. J Neurosci Res. 2007. PMID: 17304580
-
Involvement of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors and glutamate transporters in the slow excitatory synaptic transmission in the spinal cord dorsal horn.Neuroscience. 2008 Jul 17;154(4):1372-87. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.04.059. Epub 2008 May 3. Neuroscience. 2008. PMID: 18554818
-
Spinal dorsal horn synaptic plasticity: involvement of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors.Prog Brain Res. 2000;129:115-34. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(00)29009-2. Prog Brain Res. 2000. PMID: 11098685 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Novel insight into atogepant mechanisms of action in migraine prevention.Brain. 2024 Aug 1;147(8):2884-2896. doi: 10.1093/brain/awae062. Brain. 2024. PMID: 38411458 Free PMC article.
-
Glycine Transporter 1 Inhibitors: Predictions on Their Possible Mechanisms in the Development of Opioid Analgesic Tolerance.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 12;12(2):421. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020421. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38398023 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chiechio S. Modulation of chronic pain by metabotropic glutamate receptors. Adv Pharmacol 2016; 75: 63–89. - PubMed
-
- Glasauer SMK, Wäger R, Gesemann M, Neuhauss SCF. mglur6b:EGFP Transgenic zebrafish suggest novel functions of metabotropic glutamate signaling in retina and other brain regions. J Comp Neurol 2016; 524: 2363–2378. - PubMed
-
- Osikowicz M, Mika J, Przewlocka B. The glutamatergic system as a target for neuropathic pain relief. Exp Physiol 2013; 98: 372–384. - PubMed
-
- Neugebauer V, Chen PS, Willis WD. Role of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR1 in brief nociception and central sensitization of primate STT cells. J Neurophysiol 1999; 82: 272–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

