Afatinib, an EGFR inhibitor, decreases EMT and tumorigenesis of Huh‑7 cells by regulating the ERK‑VEGF/MMP9 signaling pathway
- PMID: 31432165
- PMCID: PMC6755195
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10562
Afatinib, an EGFR inhibitor, decreases EMT and tumorigenesis of Huh‑7 cells by regulating the ERK‑VEGF/MMP9 signaling pathway
Abstract
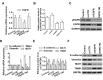
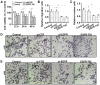
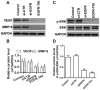
Transcatheter arterial embolization (TAE) therapy has been used in the treatment of inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, tumor recurrence and metastasis are common in patients after TAE, and these processes may be caused by circulating tumor cells (CTCs). Epithelial‑mesenchymal transition (EMT) serves important roles in CTCs, and abnormal expression and activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is common in cancer cells. Afatinib is an EGFR‑tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI). The present study aimed to investigate the effects of afatinib on EMT and tumorigenesis in HCC cells. Western blot analysis suggested that afatinib was able to effectively suppress overactivation of EGFR. Moreover, the expression levels of EMT‑ and metastasis‑associated genes were found to be modulated by afatinib through EGFR inhibition. In addition, Cell Counting Kit‑8 and Transwell assays suggested that the viability, migration and invasion of HCC cells were inhibited by afatinib through EGFR inhibition. Furthermore, the activity of the ERK signaling pathway and the expression levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9) were decreased following treatment with afatinib in vitro. Collectively, the present results suggested that the inhibitory effects of afatinib on EMT and tumorigenesis may be associated with the ERK‑VEGF/MMP9 signaling pathway. The present study provides new insights into understanding the mechanism underlying HCC and may facilitate the development of novel therapeutic strategies to treat HCC recurrence.
Figures
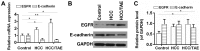
Similar articles
-
Delphinidin inhibits epidermal growth factor-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Jun;120(6):9887-9899. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28271. Epub 2018 Dec 9. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30537288
-
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transformation Promotes the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma through NF-κB/MMP9 Axis.Discov Med. 2024 Apr;36(183):666-677. doi: 10.24976/Discov.Med.202436183.63. Discov Med. 2024. PMID: 38665016
-
Ethoxy-erianin phosphate and afatinib synergistically inhibit liver tumor growth and angiogenesis via regulating VEGF and EGFR signaling pathways.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 1;438:115911. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2022.115911. Epub 2022 Feb 7. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35143806
-
Application of EGFR inhibitor reduces circulating tumor cells during transcatheter arterial embolization.Clin Transl Oncol. 2018 May;20(5):639-646. doi: 10.1007/s12094-017-1761-8. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Clin Transl Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29022239 Review.
-
MMP9: A Tough Target for Targeted Therapy for Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 6;14(7):1847. doi: 10.3390/cancers14071847. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406619 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Mechanism and Targeted Therapeutic Approaches.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1450:93-102. doi: 10.1007/5584_2023_781. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 37452258 Review.
-
Particulate matter promotes cancer metastasis through increased HBEGF expression in macrophages.Exp Mol Med. 2022 Nov;54(11):1901-1912. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00886-x. Epub 2022 Nov 9. Exp Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36352257 Free PMC article.
-
Potential benefit of osismertinib plus bevacizumab in leptomeningeal metastasis with EGFR mutant non-small-cell lung cancer.J Transl Med. 2022 Mar 14;20(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03331-9. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35287683 Free PMC article.
-
Click-based amplification: designed to facilitate various target labelling modes with ultralow background amplification.RSC Chem Biol. 2021 Mar 20;2(3):906-916. doi: 10.1039/d1cb00002k. eCollection 2021 Jun 1. RSC Chem Biol. 2021. PMID: 34458817 Free PMC article.
-
Relevance of EGFR Between Serum VEGF and MMP-9 in Primary Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients with Transarterial Chemoembolization.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Sep 23;13:9407-9417. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S257271. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 33061427 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

