A prognostic 10-lncRNA expression signature for predicting the risk of tumour recurrence in breast cancer patients
- PMID: 31429520
- PMCID: PMC6787455
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14556
A prognostic 10-lncRNA expression signature for predicting the risk of tumour recurrence in breast cancer patients
Abstract
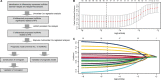
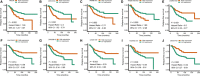
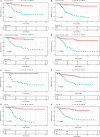
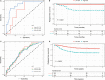
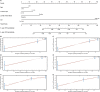
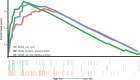
Breast cancer is one of the most frequently diagnosed malignancies and a leading cause of cancer death among females. Multiple molecular alterations are observed in breast cancer. LncRNA transcripts were proved to play important roles in the biology of tumorigenesis. In this study, we aimed to identify lncRNA expression signature that can predict breast cancer patient survival. We developed a 10-lncRNA signature-based risk score which was used to separate patients into high-risk and low-risk groups. Patients in the low-risk group had significantly better survival than those in the high-risk group. Receiver operating characteristic analysis indicated that this signature exhibited excellent diagnostic efficiency for 1-, 3- and 5-year disease-relapse events. Moreover, multivariate Cox regression analysis demonstrated that this 10-lncRNA signature was an independent risk factor when adjusting for several clinical signatures such as age, tumour size and lymph node status. The prognostic value of risk scores was validated in the validation set. In addition, a nomogram was established and the calibration plots analysis indicated the good performance and clinical utility of the nomogram. In conclusion, our results demonstrated that this 10-lncRNA signature effectively grouped patients at low and high risk of disease recurrence.
Keywords: GEO; breast cancer; lncRNA; nomogram; prognosis.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A prognostic eight-lncRNA expression signature in predicting recurrence of ER-positive breast cancer receiving endocrine therapy.J Cell Physiol. 2020 May;235(5):4746-4755. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29352. Epub 2019 Oct 29. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31663114
-
A lncRNA prognostic signature associated with immune infiltration and tumour mutation burden in breast cancer.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Nov;24(21):12444-12456. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15762. Epub 2020 Sep 23. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32967061 Free PMC article.
-
Six-long non-coding RNA signature predicts recurrence-free survival in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Jan 14;25(2):220-232. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i2.220. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30670911 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a New Eight-Long Noncoding RNA Molecular Signature for Breast Cancer Survival Prediction.DNA Cell Biol. 2019 Dec;38(12):1529-1539. doi: 10.1089/dna.2019.5059. Epub 2019 Oct 24. DNA Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31647329
-
Identification of a 6-lncRNA prognostic signature based on microarray re-annotation in gastric cancer.Cancer Med. 2020 Jan;9(1):335-349. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2621. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 31743579 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic value of seven biomarkers for breast cancer: an overview with evidence mapping and indirect comparisons of diagnostic test accuracy.Clin Exp Med. 2020 Feb;20(1):97-108. doi: 10.1007/s10238-019-00598-z. Epub 2020 Jan 1. Clin Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 31894424
-
Molecular characterization of breast cancer: a potential novel immune-related lncRNAs signature.J Transl Med. 2020 Nov 7;18(1):416. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02578-4. J Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 33160384 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulated N6-Methyladenosine RNA in Peripheral Blood: Potential Diagnostic Biomarker for Breast Cancer.Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Apr;53(2):399-408. doi: 10.4143/crt.2020.870. Epub 2020 Oct 27. Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 33138349 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of genomic instability related lncRNA signature with prognostic value and its role in cancer immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer.Front Genet. 2022 Sep 2;13:990661. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.990661. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36118868 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer survival prediction and analysis of resistance-related genes introduction.PeerJ. 2021 Oct 26;9:e12202. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12202. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34760348 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394‐424. - PubMed
-
- O'Shaughnessy J. Extending survival with chemotherapy in metastatic breast cancer. Oncologist. 2005;10(Suppl 3):20‐29. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

