Circulating plasma circular RNAs as novel diagnostic biomarkers for congenital heart disease in children
- PMID: 31429492
- PMCID: PMC6868410
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.22998
Circulating plasma circular RNAs as novel diagnostic biomarkers for congenital heart disease in children
Abstract
Objective: The diagnostic value of circulating circular RNAs (circRNAs) has received more and more attention. However, little has been reported about their potential in the diagnosis of congenital heart diseases (CHD). In this study, we explored differential expression of circRNAs from children with CHD to evaluate their potential as clinical biomarkers.
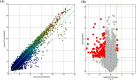
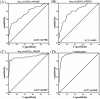
Methods: We established a discovery cohort (four CHD cases; four matched healthy controls) and a validation cohort (40 CHD cases; 40 matched healthy controls). Microarray expression analysis was performed on the discovery set to identify candidate circRNAs. Candidates were further validated in the validation set. The diagnostic accuracy of circRNAs was determined by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. Gene ontology (GO), pathway, and network analysis were performed to predict a network of circRNA/miRNA and target mRNAs related to CHD.
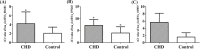
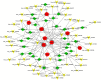
Results: The top seven significantly differentially expressed CHD-associated circRNAs were validated by RT-PCR as follows: hsa_circRNA_004183, hsa_circRNA_079265, hsa_circRNA_105039, hsa_circRNA_404686, hsa_circRNA_101050, hsa_circRNA_100787, and hsa_circRNA_101328. Three significantly down-regulated circRNAs (hsa_circRNA_004183, hsa_circRNA_079265, and hsa_circRNA_105039) were identified with area under curve (AUC) values of 0.758, 0.809, and 0.907, respectively; the combination had an AUC of 0.965. An interaction network was constructed by 43 circRNAs, 9 miRNAs, and 29 mRNAs, which involved in heart development.
Conclusions: We identified three circRNAs under-expressed in plasma from children with CHD. These circRNAs may be crucial in the development of CHD and may serve as novel non-invasive biomarkers for the diagnosis of CHD in children.
Keywords: biomarkers; circular RNAs; congenital heart diseases; diagnosis.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Microarray expression profile of circular RNAs and mRNAs in children with systemic lupus erythematosus.Clin Rheumatol. 2019 May;38(5):1339-1350. doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-4392-8. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Clin Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 30628013
-
A two-circular RNA signature as a noninvasive diagnostic biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma.J Transl Med. 2019 Feb 18;17(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-1800-z. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 30777071 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analyses reveal hsa_circ_0028883 as a diagnostic biomarker in active tuberculosis.Infect Genet Evol. 2020 Sep;83:104323. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104323. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Infect Genet Evol. 2020. PMID: 32305357
-
Identification of circRNA biomarkers in osteosarcoma: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 Jan 11;9(2):341-349. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.01.007. eCollection 2024 Jun. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 38505307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the association between circRNA expression and pediatric obesity based on a case-control study and related bioinformatics analysis.BMC Pediatr. 2023 Nov 13;23(1):561. doi: 10.1186/s12887-023-04261-1. BMC Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37957626 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Posttranscriptional Regulation by Proteins and Noncoding RNAs.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1441:313-339. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-44087-8_17. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38884719
-
Circular RNAs in Cardiovascular Diseases: Regulation and Therapeutic Applications.Research (Wash D C). 2023;6:0038. doi: 10.34133/research.0038. Epub 2023 Jan 13. Research (Wash D C). 2023. PMID: 37040523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNAs in Cardiac Regeneration: Cardiac Cell Proliferation, Differentiation, Survival, and Reprogramming.Front Physiol. 2020 Sep 29;11:580465. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.580465. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33117197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNAs as novel potential biomarkers for pancreatic cancer.J Cancer. 2021 Jun 1;12(15):4604-4615. doi: 10.7150/jca.58640. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34149924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential of using blood circular RNA as liquid biopsy biomarker for human diseases.Protein Cell. 2021 Dec;12(12):911-946. doi: 10.1007/s13238-020-00799-3. Epub 2020 Nov 1. Protein Cell. 2021. PMID: 33131025 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Larsen SH, Emmertsen K, Johnsen SP, Pedersen J, Hjortholm K, Hjortdal VE. Survival and morbidity following congenital heart surgery in a population‐basedcohort of children–up to 12 years of follow‐up. Congenit Heart Dis. 2011;6:322‐329. - PubMed
-
- Hu Z, Yuan X, Rao K, Zheng Z, Hu S. National trend in congenital heart diseasemortality in China during 2003 to 2010: a population‐based study. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;148:596‐602. - PubMed
-
- Zhuang J. The continuing challenge of congenital heart disease in China. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015;150:738. - PubMed
-
- Holland BJ, Myers JA, Woods CR Jr. Prenatal diagnosis of critical congenitalheart disease reduces risk of death from cardiovascular compromise prior toplanned neonatal cardiac surgery: a meta‐analysis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2015;45:631‐638. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

