Rapamycin-upregulated miR-29b promotes mTORC1-hyperactive cell growth in TSC2-deficient cells by downregulating tumor suppressor retinoic acid receptor β (RARβ)
- PMID: 31420607
- PMCID: PMC6895402
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-019-0957-5
Rapamycin-upregulated miR-29b promotes mTORC1-hyperactive cell growth in TSC2-deficient cells by downregulating tumor suppressor retinoic acid receptor β (RARβ)
Abstract
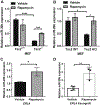
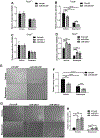
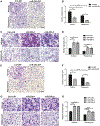
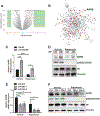
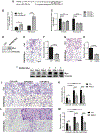
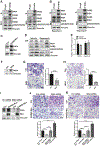
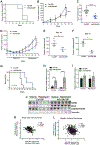
miR-29b has been identified as a rapamycin-induced microRNA (miRNA) in Tsc2-deficient, mTORC1-hyperactive cells. The biological significance of this induction of miR-29b is unknown. We have found that miR-29b acts as an oncogenic miRNA in Tsc2-deficient cells: inhibition of miR-29b suppressed cell proliferation, anchorage-independent cell growth, cell migration, invasion, and the growth of Tsc2-deficient tumors in vivo. Importantly, the combination of miR-29b inhibition with rapamycin treatment further inhibited these tumor-associated cellular processes. To gain insight into the molecular mechanisms by which miR-29b promotes tumorigenesis, we used RNA sequencing to identify the tumor suppressor retinoid receptor beta (RARβ) as a target gene of miR-29b. We found that miR-29b directly targeted the 3'UTR of RARβ. Forced expression of RARβ reversed the effects of miR-29b overexpression in proliferation, migration, and invasion, indicating that it is a critical target. miR-29b expression correlated with low RARβ expression in renal clear cell carcinomas and bladder urothelial carcinomas, tumors associated with TSC gene mutations. We further identified growth family member 4 (ING4) as a novel interacting partner of RARβ. Overexpression of ING4 inhibited the migration and invasion of Tsc2-deficient cells while silencing of ING4 reversed the RARβ-mediated suppression of cell migration and invasion. Taken together, our findings reveal a novel miR-29b/RARβ/ING4 pathway that regulates tumorigenic properties of Tsc2-deficient cells, and that may serve as a potential therapeutic target for TSC, lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM), and other mTORC1-hyperactive tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Upregulation of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase (PFKFB3) by hyperactivated mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 is critical for tumor growth in tuberous sclerosis complex.IUBMB Life. 2020 May;72(5):965-977. doi: 10.1002/iub.2232. Epub 2020 Jan 20. IUBMB Life. 2020. PMID: 31958214
-
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) is critical for progression of tuberous sclerosis complex 2 (TSC2)-deficient tumors.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 15;292(50):20528-20543. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.799593. Epub 2017 Sep 27. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28972182 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-21 is induced by rapamycin in a model of tuberous sclerosis (TSC) and lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM).PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e60014. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060014. Epub 2013 Mar 29. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23555865 Free PMC article.
-
Mir-29b in Breast Cancer: A Promising Target for Therapeutic Approaches.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Sep 2;12(9):2139. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12092139. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36140539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The miR-29 family in hematological malignancies.Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2015 Jun;159(2):184-91. doi: 10.5507/bp.2014.037. Epub 2014 Jul 4. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2015. PMID: 25004911 Review.
Cited by
-
Vitamin A and Retinoids in Bladder Cancer Chemoprevention and Treatment: A Narrative Review of Current Evidence, Challenges and Future Prospects.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 29;22(7):3510. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073510. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33805295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of CK2/ING4 Pathway Facilitates Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Immunotherapy.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Dec;10(34):e2304068. doi: 10.1002/advs.202304068. Epub 2023 Oct 23. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37870169 Free PMC article.
-
CrossTORC and WNTegration in Disease: Focus on Lymphangioleiomyomatosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 24;22(5):2233. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052233. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33668092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Roles for Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Complexes in Bladder Cancer Progression and Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 18;14(6):1555. doi: 10.3390/cancers14061555. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retinoic acid and microRNA.Methods Enzymol. 2020;637:283-308. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2020.02.009. Epub 2020 Mar 28. Methods Enzymol. 2020. PMID: 32359650 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

