Identification of Key Genes and Pathways in Pancreatic Cancer Gene Expression Profile by Integrative Analysis
- PMID: 31412643
- PMCID: PMC6722756
- DOI: 10.3390/genes10080612
Identification of Key Genes and Pathways in Pancreatic Cancer Gene Expression Profile by Integrative Analysis
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic cancer is one of the malignant tumors that threaten human health.
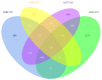
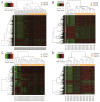
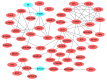
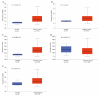
Methods: The gene expression profiles of GSE15471, GSE19650, GSE32676 and GSE71989 were downloaded from the gene expression omnibus database including pancreatic cancer and normal samples. The differentially expressed genes between the two types of samples were identified with the Limma package using R language. The gene ontology functional and pathway enrichment analyses of differentially-expressed genes were performed by the DAVID software followed by the construction of a protein-protein interaction network. Hub gene identification was performed by the plug-in cytoHubba in cytoscape software, and the reliability and survival analysis of hub genes was carried out in The Cancer Genome Atlas gene expression data.
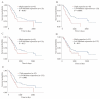
Results: The 138 differentially expressed genes were significantly enriched in biological processes including cell migration, cell adhesion and several pathways, mainly associated with extracellular matrix-receptor interaction and focal adhesion pathway in pancreatic cancer. The top hub genes, namely thrombospondin 1, DNA topoisomerase II alpha, syndecan 1, maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase and proto-oncogene receptor tyrosine kinase Met were identified from the protein-protein interaction network. The expression levels of hub genes were consistent with data obtained in The Cancer Genome Atlas. DNA topoisomerase II alpha, syndecan 1, maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase and proto-oncogene receptor tyrosine kinase Met were significantly linked with poor survival in pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
Conclusions: These hub genes may be used as potential targets for pancreatic cancer diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: bioinformatics; gene expression; hub gene; pancreatic cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of candidate biomarkers and pathways associated with SCLC by bioinformatics analysis.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Aug;18(2):1538-1550. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9095. Epub 2018 May 29. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29845250 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of hub genes and regulators associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma based on integrated gene expression profile analysis.Discov Med. 2019 Sep;28(153):159-172. Discov Med. 2019. PMID: 31926587
-
Identification of novel genes associated with a poor prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via a bioinformatics analysis.Biosci Rep. 2019 Aug 2;39(8):BSR20190625. doi: 10.1042/BSR20190625. Print 2019 Aug 30. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31311829 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of key genes in prostate cancer gene expression profile by bioinformatics.Andrologia. 2019 Feb;51(1):e13169. doi: 10.1111/and.13169. Epub 2018 Oct 11. Andrologia. 2019. PMID: 30311263
-
Screening and identification of hub genes in pancreatic cancer by integrated bioinformatics analysis.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Dec;120(12):19496-19508. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29253. Epub 2019 Jul 11. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31297881
Cited by
-
Identification of prognostic risk factors for pancreatic cancer using bioinformatics analysis.PeerJ. 2020 Jun 15;8:e9301. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9301. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32587798 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics analysis of key biomarkers for bladder cancer.Biomed Rep. 2022 Dec 16;18(2):14. doi: 10.3892/br.2022.1596. eCollection 2023 Feb. Biomed Rep. 2022. PMID: 36643693 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of miR-199a-3p in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Its Relevant Molecular Mechanism via GEO, TCGA Database and In Silico Analyses.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1533033820979670. doi: 10.1177/1533033820979670. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 33327879 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of key genes and pathways in mild and severe nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by integrative analysis.Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2021 Sep 14;7(4):276-286. doi: 10.1016/j.cdtm.2021.08.002. eCollection 2021 Dec. Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34786546 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analysis identifies a pathway-related competing endogenous RNA network in the progression of pancreatic cancer.BMC Cancer. 2020 Oct 2;20(1):958. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07470-4. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33008376 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

