A human-on-a-chip approach to tackling rare diseases
- PMID: 31412288
- PMCID: PMC6856435
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2019.08.001
A human-on-a-chip approach to tackling rare diseases
Abstract
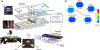
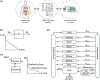
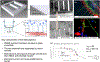
Drug development for rare diseases, classified as diseases with a prevalence of < 200 000 patients, is limited by the high cost of research and low target population. Owing to a lack of representative disease models, research has been challenging for orphan drugs. Human-on-a-chip (HoaC) technology, which models human tissues in interconnected in vitro microfluidic devices, has the potential to lower the cost of preclinical studies and increase the rate of drug approval by introducing human phenotypic models early in the drug discovery process. Advances in HoaC technology can drive a new approach to rare disease research and orphan drug development.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Drug labels: a flawed source of data for studying orphan drug approvals.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012 Dec;92(6):694; author reply 695. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2012.166. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012. PMID: 23073207 No abstract available.
-
Microphysiological Systems (Tissue Chips) and their Utility for Rare Disease Research.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1031:405-415. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-67144-4_23. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29214585 Review.
-
Raising orphans: how clinical development programs of drugs for rare and common diseases are different.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012 Aug;92(2):262-4. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2012.87. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22739137
-
Accelerating orphan drug development.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010 Dec;9(12):901-2. doi: 10.1038/nrd3340. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010. PMID: 21119719
-
[Orphan drugs : New opportunities for the treatment of rare diseases].Internist (Berl). 2016 Nov;57(11):1132-1138. doi: 10.1007/s00108-016-0114-y. Internist (Berl). 2016. PMID: 27527064 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Optimization of Application-Driven Development of In Vitro Neuromuscular Junction Models.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2022 Dec;28(6):1180-1191. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2021.0204. Epub 2022 Aug 1. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2022. PMID: 35018825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organ-on-a-Chip: A New Paradigm for Drug Development.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Feb;42(2):119-133. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2020.11.009. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33341248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Building Blood Vessel Chips with Enhanced Physiological Relevance.Adv Mater Technol. 2023 Apr 6;8(7):2201778. doi: 10.1002/admt.202201778. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Adv Mater Technol. 2023. PMID: 37693798 Free PMC article.
-
Tackling Current Biomedical Challenges With Frontier Biofabrication and Organ-On-A-Chip Technologies.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Sep 16;9:732130. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.732130. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34604190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex in vitro Model: A Transformative Model in Drug Development and Precision Medicine.Clin Transl Sci. 2023 Dec 7;17(2):e13695. doi: 10.1111/cts.13695. Online ahead of print. Clin Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 38062923 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cheung RY et al. (2004) Orphan drug policies: implications for the United States, Canada, and developing countries. Health Law J 12, 183–200 - PubMed
-
- Mullard A (2016) Parsing clinical success rates. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 15, 447 - PubMed
-
- Schieppati A et al. (2008) Why rare diseases are an important medical and social issue. Lancet 371, 2039–2041 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

