Distinct Modified Nucleosides in tRNATrp from the Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis and Requirement of tRNA m2G10/m22G10 Methyltransferase (Archaeal Trm11) for Survival at High Temperatures
- PMID: 31405913
- PMCID: PMC6779453
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00448-19
Distinct Modified Nucleosides in tRNATrp from the Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis and Requirement of tRNA m2G10/m22G10 Methyltransferase (Archaeal Trm11) for Survival at High Temperatures
Abstract
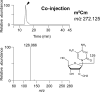
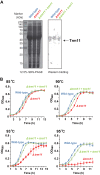
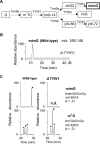
tRNA m2G10/m22G10 methyltransferase (archaeal Trm11) methylates the 2-amino group in guanosine at position 10 in tRNA and forms N2,N2-dimethylguanosine (m22G10) via N2-methylguanosine (m2G10). We determined the complete sequence of tRNATrp, one of the substrate tRNAs for archaeal Trm11 from Thermococcus kodakarensis, a hyperthermophilic archaeon. Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry following enzymatic digestion of tRNATrp identified 15 types of modified nucleoside at 21 positions. Several modifications were found at novel positions in tRNA, including 2'-O-methylcytidine at position 6, 2-thiocytidine at position 17, 2'-O-methyluridine at position 20, 5,2'-O-dimethylcytidine at position 32, and 2'-O-methylguanosine at position 42. Furthermore, methylwyosine was found at position 37 in this tRNATrp, although 1-methylguanosine is generally found at this location in tRNATrp from other archaea. We constructed trm11 (Δtrm11) and some gene disruptant strains and compared their tRNATrp with that of the wild-type strain, which confirmed the absence of m22G10 and other corresponding modifications, respectively. The lack of 2-methylguanosine (m2G) at position 67 in the trm11 trm14 double disruptant strain suggested that this methylation is mediated by Trm14, which was previously identified as an m2G6 methyltransferase. The Δtrm11 strain grew poorly at 95°C, indicating that archaeal Trm11 is required for T. kodakarensis survival at high temperatures. The m22G10 modification might have effects on stabilization of tRNA and/or correct folding of tRNA at the high temperatures. Collectively, these results provide new clues to the function of modifications and the substrate specificities of modification enzymes in archaeal tRNA, enabling us to propose a strategy for tRNA stabilization of this archaeon at high temperatures.IMPORTANCEThermococcus kodakarensis is a hyperthermophilic archaeon that can grow at 60 to 100°C. The sequence of tRNATrp from this archaeon was determined by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Fifteen types of modified nucleoside were observed at 21 positions, including 5 modifications at novel positions; in addition, methylwyosine at position 37 was newly observed in an archaeal tRNATrp The construction of trm11 (Δtrm11) and other gene disruptant strains confirmed the enzymes responsible for modifications in this tRNA. The lack of 2-methylguanosine (m2G) at position 67 in the trm11 trm14 double disruptant strain suggested that this position is methylated by Trm14, which was previously identified as an m2G6 methyltransferase. The Δtrm11 strain grew poorly at 95°C, indicating that archaeal Trm11 is required for T. kodakarensis survival at high temperatures.
Keywords: archaea; gene disruption; mass spectrometry; tRNA methyltransferase; tRNA modification.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Formation of m2G6 in Methanocaldococcus jannaschii tRNA catalyzed by the novel methyltransferase Trm14.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Sep 1;39(17):7641-55. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr475. Epub 2011 Jun 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21693558 Free PMC article.
-
Archaeosine Modification of Archaeal tRNA: Role in Structural Stabilization.J Bacteriol. 2020 Mar 26;202(8):e00748-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00748-19. Print 2020 Mar 26. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 32041795 Free PMC article.
-
The TK0271 Protein Activates Transcription of Aromatic Amino Acid Biosynthesis Genes in the Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis.mBio. 2019 Sep 10;10(5):e01213-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01213-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31506306 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of 25 years of research on Thermococcus kodakarensis, a genetically versatile model organism for archaeal research.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2020 Feb;65(1):67-78. doi: 10.1007/s12223-019-00730-2. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2020. PMID: 31286382 Review.
-
7-Methylguanosine Modifications in Transfer RNA (tRNA).Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 17;19(12):4080. doi: 10.3390/ijms19124080. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30562954 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The extensive m5C epitranscriptome of Thermococcus kodakarensis is generated by a suite of RNA methyltransferases that support thermophily.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 23;15(1):7272. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51410-w. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39179532 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional insights into Archaeoglobus fulgidus m2G10 tRNA methyltransferase Trm11 and its Trm112 activator.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Nov 4;48(19):11068-11082. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa830. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 33035335 Free PMC article.
-
Required Elements in tRNA for Methylation by the Eukaryotic tRNA (Guanine-N2-) Methyltransferase (Trm11-Trm112 Complex).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 6;23(7):4046. doi: 10.3390/ijms23074046. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409407 Free PMC article.
-
N 2-methylguanosine modifications on human tRNAs and snRNA U6 are important for cell proliferation, protein translation and pre-mRNA splicing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Aug 11;51(14):7496-7519. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad487. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37283053 Free PMC article.
-
Epitranscriptome: Review of Top 25 Most-Studied RNA Modifications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 10;23(22):13851. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213851. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430347 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McCloskey JA, Graham DE, Zou S, Crain PF, Ibba M, Konisky J, Söll D, Olsen GJ. 2001. Post-transcriptional modification in archaeal tRNAs: identities and phylogenetic relations of nucleotides from mesophilic and hyperthermophilic Methanococcales. Nucleic Acids Res 29:4299–4706. doi:10.1093/nar/29.22.4699. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Noon KR, Guymon R, Crain PF, McCloskey JA, Thomm M, Lim J, Cavicchioli R. 2003. Influence of temperature on tRNA modification in archaea: Methanococcoides burtonii (optimum growth temperature [Topt], 23 degrees C) and Stetteria hydrogenophila (Topt, 95 degrees C). J Bacteriol 185:5483–5490. doi:10.1128/jb.185.18.5483-5490.2003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

