Necroptosis: a crucial pathogenic mediator of human disease
- PMID: 31391333
- PMCID: PMC6693822
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.128834
Necroptosis: a crucial pathogenic mediator of human disease
Abstract
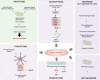
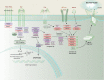
Necroptosis is a genetically regulated form of necrotic cell death that has emerged as an important pathway in human disease. The necroptosis pathway is induced by a variety of signals, including death receptor ligands, and regulated by receptor-interacting protein kinases 1 and 3 (RIPK1 and RIPK3) and mixed-lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase (MLKL), which form a regulatory necrosome complex. RIPK3-mediated phosphorylation of MLKL executes necroptosis. Recent studies, using animal models of tissue injury, have revealed that RIPK3 and MLKL are key effectors of injury propagation. This Review explores the functional roles of RIPK3 and MLKL as crucial pathogenic determinants and markers of disease progression and severity in experimental models of human disease, including acute and chronic pulmonary diseases; renal, hepatic, cardiovascular, and neurodegenerative diseases; cancer; and critical illness.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
A cytosolic heat shock protein 90 and co-chaperone p23 complex activates RIPK3/MLKL during necroptosis of endothelial cells in acute respiratory distress syndrome.J Mol Med (Berl). 2020 Apr;98(4):569-583. doi: 10.1007/s00109-020-01886-y. Epub 2020 Feb 19. J Mol Med (Berl). 2020. PMID: 32072232
-
FKBP12 mediates necroptosis by initiating RIPK1-RIPK3-MLKL signal transduction in response to TNF receptor 1 ligation.J Cell Sci. 2019 May 20;132(10):jcs227777. doi: 10.1242/jcs.227777. J Cell Sci. 2019. PMID: 31028177
-
CK1α, CK1δ, and CK1ε are necrosome components which phosphorylate serine 227 of human RIPK3 to activate necroptosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jan 28;117(4):1962-1970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1917112117. Epub 2020 Jan 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 31932442 Free PMC article.
-
Necroptosis: A Pathogenic Negotiator in Human Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 22;23(21):12714. doi: 10.3390/ijms232112714. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Insights into the Mechanism of Necroptosis: The Necrosome As a Potential Therapeutic Target.Cells. 2019 Nov 21;8(12):1486. doi: 10.3390/cells8121486. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31766571 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Release mechanisms of major DAMPs.Apoptosis. 2021 Apr;26(3-4):152-162. doi: 10.1007/s10495-021-01663-3. Epub 2021 Mar 13. Apoptosis. 2021. PMID: 33713214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Necroptosis protects against exacerbation of acute pancreatitis.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jun 10;12(6):601. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03847-w. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34112763 Free PMC article.
-
Worms, Fat, and Death: Caenorhabditis elegans Lipid Metabolites Regulate Cell Death.Metabolites. 2021 Feb 23;11(2):125. doi: 10.3390/metabo11020125. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 33672292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatic inflammation after burn injury is associated with necroptotic cell death signaling.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2020 Oct;89(4):768-774. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000002865. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2020. PMID: 33017135 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM24-RIP3 axis perturbation accelerates osteoarthritis pathogenesis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Dec;79(12):1635-1643. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217904. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020. PMID: 32895234 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

