Biomarkers of subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with psoriatic arthritis
- PMID: 31388317
- PMCID: PMC6607207
- DOI: 10.2147/OARRR.S206931
Biomarkers of subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with psoriatic arthritis
Abstract
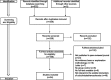
Background: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic immune-mediated disease. It is associated with an increase in cardiovascular risk factors (obesity, hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidemia), giving a higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events. Patients with PsA have an increased incidence of subclinical atherosclerosis and endothelial dysfunction. The aim of this study is to perform a review of the biomarkers of subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with PsA. Methods: A search was performed in the electronic databases (PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and Embase) up until July 2017. Studies were considered if they included data on biomarkers of subclinical atherosclerosis in PsA, and each article was then reviewed for quality and clinical relevance. After completing the literature search, all screened literature was summarized and discussed in our study group (CaRRDs study group). Results: The initial search produced 532 abstracts, which were limited to 258 potentially relevant articles by preliminary review of the titles and by excluding review articles and case reports (n=274). A further 102 articles were deemed ineligible after examining the abstracts. Full texts of the remaining 156 articles were retrieved. Most articles were excluded because they were not relevant to the biomarkers of subclinical atherosclerosis in psoriasis and/or PsA. In the end, 54 articles were deemed eligible for this review. Conclusion: Patients with PsA showed more severe atherosclerotic disease compared with patients with only psoriasis. This may have been due to the higher systemic inflammatory burden from the combination of both diseases. In patients with PsA some molecules may be considered as markers of atherosclerotic disease, and their detection may be a prognostic marker, in addition to imaging procedures, for the development of atherosclerotic disease, and could be suitable for the management of patients with PsA.
Keywords: complement C3; insulin resistance; lipid profile; primary and secondary hemostasis; psoriatic disease; serum uric acid.
Conflict of interest statement
RS, RP, LC, FC, and MNDDM have acted as paid lecturers or board members and received grants and honoraria in the past 36 months for research unrelated to the present study. RP is a member of the Editorial Board for BMC Muscoskeletal Disorders. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiovascular Risk Markers and Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Psoriatic Arthritis Patients.Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2018;13(3):199-209. doi: 10.2174/1574887113666180314105511. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2018. PMID: 29542417 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and Extent of Subclinical Atherosclerosis and Associated Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Adult Patients With Psoriatic Arthritis: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2021 Aug 3;13(8):e16853. doi: 10.7759/cureus.16853. eCollection 2021 Aug. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34513433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular comorbidities in patients with psoriatic arthritis: a systematic review.Ann Rheum Dis. 2013 Feb;72(2):211-6. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-201194. Epub 2012 Apr 24. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013. PMID: 22532629 Review.
-
Behavioral and Pharmacotherapy Weight Loss Interventions to Prevent Obesity-Related Morbidity and Mortality in Adults: An Updated Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force [Internet].Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2018 Sep. Report No.: 18-05239-EF-1. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2018 Sep. Report No.: 18-05239-EF-1. PMID: 30354042 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Features of the interconnection of traditional risk factors and il-10 with the activity of the inflammatory process and atherosclerosis development in patients with psoriatic arthritis.Wiad Lek. 2020;73(5):914-919. Wiad Lek. 2020. PMID: 32386368
Cited by
-
Arterial Stiffness as a Surrogate Marker of Cardiovascular Disease and Atherosclerosis in Patients with Arthritides and Connective Tissue Diseases: A Literature Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 May 26;13(11):1870. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13111870. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37296720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers in Psoriasis: The Future of Personalised Treatment.Indian J Dermatol. 2024 May-Jun;69(3):256-263. doi: 10.4103/ijd.ijd_167_24. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Indian J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 39119310 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive impairment in elderly patients with rheumatic disease and the effect of disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs.Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Apr;40(4):1221-1231. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05372-1. Epub 2020 Aug 30. Clin Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 32862311 Review.
-
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein associates with cardiovascular disease by a vicious cycle of atherosclerosis and inflammation: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Jan 16;9:1023651. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1023651. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 36727024 Free PMC article.
-
Persistence of C-reactive protein increased levels and high disease activity are predictors of cardiovascular disease in patients with axial spondyloarthritis.Sci Rep. 2022 May 7;12(1):7498. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11640-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35525861 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Edson-Heredia E, Zhu B, Lefevre C, et al. Prevalence and incidence rates of cardiovascular, autoimmune, and other diseases in patients with psoriatic or psoriatic arthritis: a retrospective study using clinical practice research datalink. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29(5):955–963. doi:10.1111/jdv.12669 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous