Emerging Role of l-Dopa Decarboxylase in Flaviviridae Virus Infections
- PMID: 31387309
- PMCID: PMC6721762
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8080837
Emerging Role of l-Dopa Decarboxylase in Flaviviridae Virus Infections
Abstract
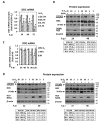
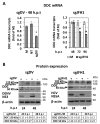
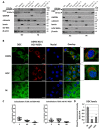
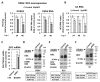
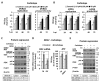
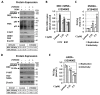
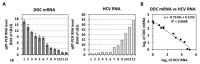
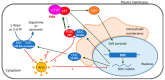
l-dopa decarboxylase (DDC) that catalyzes the biosynthesis of bioactive amines, such as dopamine and serotonin, is expressed in the nervous system and peripheral tissues, including the liver, where its physiological role remains unknown. Recently, we reported a physical and functional interaction of DDC with the major signaling regulator phosphoinosite-3-kinase (PI3K). Here, we provide compelling evidence for the involvement of DDC in viral infections. Studying dengue (DENV) and hepatitis C (HCV) virus infection in hepatocytes and HCV replication in liver samples of infected patients, we observed a negative association between DDC and viral replication. Specifically, replication of both viruses reduced the levels of DDC mRNA and the ~120 kDa SDS-resistant DDC immunoreactive functional complex, concomitant with a PI3K-dependent accumulation of the ~50 kDa DDC monomer. Moreover, viral infection inhibited PI3K-DDC association, while DDC did not colocalize with viral replication sites. DDC overexpression suppressed DENV and HCV RNA replication, while DDC enzymatic inhibition enhanced viral replication and infectivity and affected DENV-induced cell death. Consistently, we observed an inverse correlation between DDC mRNA and HCV RNA levels in liver biopsies from chronically infected patients. These data reveal a novel relationship between DDC and Flaviviridae replication cycle and the role of PI3K in this process.
Keywords: dengue virus; hepatitis C virus; l-dopa decarboxylase; phosphoinosite-3-kinase (PI3K).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
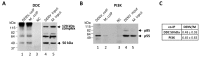
Similar articles
-
Association of Hepatitis C Virus Replication with the Catecholamine Biosynthetic Pathway.Viruses. 2021 Oct 23;13(11):2139. doi: 10.3390/v13112139. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34834946 Free PMC article.
-
L-Dopa decarboxylase modulates autophagy in hepatocytes and is implicated in dengue virus-caused inhibition of autophagy completion.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2024 Jan;1871(1):119602. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2023.119602. Epub 2023 Sep 29. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 37778471
-
Dengue Virus Replication Is Associated with Catecholamine Biosynthesis and Metabolism in Hepatocytes.Viruses. 2022 Mar 9;14(3):564. doi: 10.3390/v14030564. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35336971 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting host lipid synthesis and metabolism to inhibit dengue and hepatitis C viruses.Antiviral Res. 2015 Dec;124:110-21. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.10.013. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Antiviral Res. 2015. PMID: 26526588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dengue virus- and hepatitis C virus-induced replication and assembly compartments: the enemy inside--caught in the web.J Virol. 2014 Jun;88(11):5907-11. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03404-13. Epub 2014 Mar 12. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24623440 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association Between ADHD and COVID-19 Infection and Clinical Outcomes: A Retrospective Cohort Study From Electronic Medical Records.J Atten Disord. 2023 Jan;27(2):169-181. doi: 10.1177/10870547221129305. Epub 2022 Oct 20. J Atten Disord. 2023. PMID: 36264064 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Human L-Dopa Decarboxylase (DDC) under Conditions of Oxidative Stress.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Dec 16;45(12):10179-10192. doi: 10.3390/cimb45120635. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 38132481 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro and In Silico Anti-Arboviral Activities of Dihalogenated Phenolic Derivates of L-Tyrosine.Molecules. 2021 Jun 5;26(11):3430. doi: 10.3390/molecules26113430. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34198817 Free PMC article.
-
Novel polymorphisms of dopa decarboxylase gene and their association with lamb quality traits in Indonesian sheep.Anim Biosci. 2023 Jun;36(6):840-850. doi: 10.5713/ab.22.0227. Epub 2022 Nov 14. Anim Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36397687 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Hepatitis C Virus Replication with the Catecholamine Biosynthetic Pathway.Viruses. 2021 Oct 23;13(11):2139. doi: 10.3390/v13112139. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34834946 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adam W.R., Culvenor A.J., Hall J., Jarrott B., Wellard R.M. Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase: Histochemical localization in rat kidney and lack of effect of dietary potassium or sodium loading on enzyme distribution. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Phys. 1986;13:47–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1986.tb00314.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

