LINC00472 Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in NSCLC through KLLN-Mediated p53-Signaling Pathway via MicroRNA-149-3p and MicroRNA-4270
- PMID: 31382188
- PMCID: PMC6676247
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.06.003
LINC00472 Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in NSCLC through KLLN-Mediated p53-Signaling Pathway via MicroRNA-149-3p and MicroRNA-4270
Retraction in
-
Retraction Notice to: LINC00472 Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in NSCLC through KLLN-Mediated p53-Signaling Pathway via MicroRNA-149-3p and MicroRNA-4270.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022 May 10;28:597. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.05.016. eCollection 2022 Jun 14. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022. PMID: 35614992 Free PMC article.
Abstract
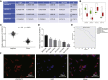
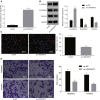
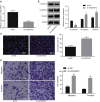
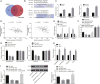
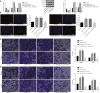
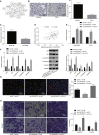
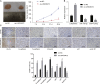
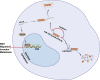
Long non-coding RNAs and microRNAs (miRNAs) have been reported to participate in the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Long intergenic non-protein-coding RNA 472 (LINC00472), miR-149-3p, and miR-4270 were found to be involved in tumor activities, suggesting potential roles in NSCLC. Thus, this study aimed to examine the ability of LINC00472 to influence the progression of NSCLC with the involvement of miR-149-3p and miR-4270. Initially, differentially expressed long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), downstream regulatory miRNAs, and genes related to NSCLC were identified. Next, the interaction among LINC00472, miR-149-3p and miR-4270, and KLLN and the p53-signaling pathway was determined. The effect of LINC00472 on the expression of E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and Vimentin was examined through gain-of-function and loss-of-function experiments. Lastly, the effects of LINC00472 on NSCLC tumor growth were assessed in vivo. LINC00472 and KLLN were found to exhibit low levels, while miR-149-3p and miR-4270 were highly expressed in NSCLC. In addition, the overexpression of LINC00472 was observed to upregulate KLLN and activate the p53-signaling pathway, which ultimately inhibited the invasion, migration, and EMT of NSCLC cells via miR-149-3p and miR-4270, corresponding to decreased N-cadherin and Vimentin and increased E-cadherin. The overexpression of LINC00472 exerted an inhibitory effect on tumor growth in vivo. Taken together, the key evidence suggests that the overexpression of LINC00472 can downregulate miR-149-3p and miR-4270 to upregulate KLLN and activate the p53-signaling pathway, thus inhibiting the development of NSCLC. This study highlights the potential of LINC00472 as a promising therapeutic target for NSCLC treatment.
Keywords: KLLN; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; invasion; long intergenic non-protein-coding RNA 472; microRNA-149-3p; microRNA-4270; migration; non-small-cell lung cancer; p53-signaling pathway.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LncRNA-LINC00472 suppresses the malignant progression of non-small cell lung cancer via modulation of the miRNA-1275/Homeobox A2 axis.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2024 Mar;33(3):283-297. doi: 10.17219/acem/168431. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 37665081
-
Downregulation of N-Acetylglucosaminyltransferase GCNT3 by miR-302b-3p Decreases Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(3):987-1004. doi: 10.1159/000494482. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30355927
-
Retraction Notice to: LINC00472 Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in NSCLC through KLLN-Mediated p53-Signaling Pathway via MicroRNA-149-3p and MicroRNA-4270.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022 May 10;28:597. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.05.016. eCollection 2022 Jun 14. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022. PMID: 35614992 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-338-3p suppresses metastasis of lung cancer cells by targeting the EMT regulator Sox4.Am J Cancer Res. 2016 Jan 15;6(2):127-40. eCollection 2016. Am J Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27186391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review on the role of LINC00472 in malignant and non-malignant disorders.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Jul;247:154549. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154549. Epub 2023 May 18. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37235910 Review.
Cited by
-
Crosstalk between Circulatory Microenvironment and Vascular Endothelial Cells in Acute Myocardial Infarction.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Oct 29;14:5597-5610. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S316414. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34744446 Free PMC article.
-
LINC00472 suppressed by ZEB1 regulates the miR-23a-3p/FOXO3/BID axis to inhibit the progression of pancreatic cancer.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Sep;25(17):8312-8328. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16784. Epub 2021 Aug 7. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34363438 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of miR-4270 Suppression on Migration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Line (HepG2).Iran Biomed J. 2023 Jul 1;27(4):167-72. doi: 10.61186/ibj.3923. Iran Biomed J. 2023. PMID: 37430248 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation-dependent MCM6 repression induced by LINC00472 inhibits triple-negative breast cancer metastasis by disturbing the MEK/ERK signaling pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Feb 26;13(4):4962-4975. doi: 10.18632/aging.103568. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33668040 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA LINC00472 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via miR-4311/GNG7 axis.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):6371-6382. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2040768. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35240924 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang Z.X., Bian H.B., Wang J.R., Cheng Z.X., Wang K.M., De W. Prognostic significance of serum miRNA-21 expression in human non-small cell lung cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2011;104:847–851. - PubMed
-
- Maeda R., Yoshida J., Hishida T., Aokage K., Nishimura M., Nishiwaki Y., Nagai K. Late recurrence of non-small cell lung cancer more than 5 years after complete resection: incidence and clinical implications in patient follow-up. Chest. 2010;138:145–150. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

